With exploits and vulnerabilities revealed almost daily and reports of cyber-crimes increasing, security is on everyone’s minds. There are different ways you can go about improving your system security. If you use (or plan to use) a CentOS or Fedora server, SELinux is an ideal starting point. SELinux is a fast and robust security protocol and application that helps you check and control the users and their access level to the files and applications on the system. In this article, I’ll provide a brief intro to SELinux before showing you how to enable SELinux on CentOS 7.
What is SELinux?
The Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) is a security structure designed to provide Linux system administrators with more control over users accessing the system. It was originally developed by the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) as a series of patches and upgrades to the Linux kernel using the Linux Security Modules (LSM). SELinux was released as an open-source tool in 2000 and then synced with the whole Linux Kernel in 2003.
How Does SELinux Work?
SELinux controls access to all the files, processes, and applications on your system. Using a set of predefined rules as the security policies, SELinux can define a secure and valuable access policy. SELinux, will protect the system and prevent unauthorized attempts to access a resource. In this approach, the so-called principle of least privilege means that the user of a program needs to be granted permission to access files, directories, sockets, and other services.
When an application or process (called a “subject”) requests to access a file as an object, SELinux uses the Access Vector Cache (AVC) to evaluate the access. This cache stores all the permission caches for subjects and objects, which means the processes and what they’re trying to access. Without any permission caches stored, SELinux wouldn’t be able to make any decisions. In such cases, SELinux simply contacts the security server and asks for information to evaluate the access request. The security server applies the SELinux policy for evaluating the access, then grants or denies the request based on that. You can always check out the message logs (at “/var/log.messages”) to see which requests have been accepted or denied.
What Are The SELinux Modes?
SELinux allows admins to set its functionality to one of the three following modes. Each mode has different security restrictions and its uses:
Enforcing mode: This is the default mode, which blocks and logs the actions that don’t meet the policy standards.
Permissive mode: This mode provides you with the ability to work on logs and events in detail. This mode especially helps test the SELinux feature. Here, changing modes of operation between the forced and the permissive will not require a system reboot.
Disabled mode: This allows you to perform all actions and do not log the action. Switching to this mode requires a system reboot.
How to Enable SElinux in CentOS 7
-
Check The SELinux Status :
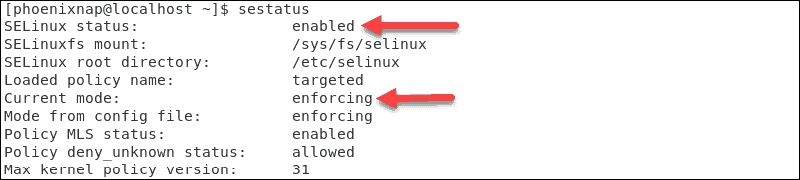
Step 1: Check your SELinux On/Off Status
Before trying to enable SELinux, you should check if it’s already disabled.
Enter the following command check the settings in your terminal:
sestatus
The output shows that SELinux is now disabled on your system.
Step 2: Check your Requirements for Enabling SELinux
- A user account with the sudo privileges
- Access to a terminal/console
- A system based RHEL like CentOS 7
- A text editor tool nano
Want a better way to host your websites and web apps? Developing something new? Simply don’t like Windows? That’s why we have Linux VPS. Linux Hosting Simplified
Linux Hosting Simplified
-
Starting SELinux :
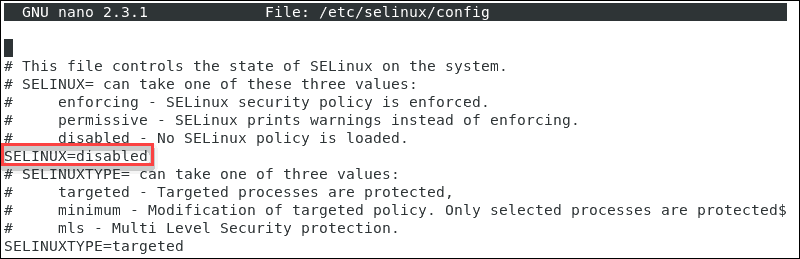
Step 3: Use nano editor to open the Config file
Set the SELinux status of the service. So go to /etc/selinux/config file and use a text editor like Nano.
sudo nano /etc/selinux/config
Step 4: Change SELinux Mode
Now, you can change the SELinux mode to either permissive or enforcing.
Here you can change the marked line to the mode you need.
Step 5: Save the Changes
Then press CTRL + X to apply and save. After that, press ‘y’, then Enter to confirm the whole process
Step 6: Reboot your Server
Now you should reboot the system. To do so, enter the command below and press <Enter>:
sudo reboot
Step 7: Re-Check SELinux Status
If you want to check the status of SELinux, enter “sestatus” in the command line again.
Now, the result confirms that you’ve already enabled the enforcing mode in the system.
How to Disable SELinux on CentOS 7
Follow the command below to switch the SELinux mode temporarily from targeted to permissive::
sudo setenforce
But notice that this change only applies to the current runtime session.
To disable SELinux on your CentOS 7 system permanently, follow these steps:
Step 1: Set SELinux mode to “disabled”
Open the /etc/selinux/config file, then you should set the SELINUX mode to “disabled”
Step 2: Save Changes and Reboot
Now save the file and after that, reboot your CentOS system with the command:
sudo shutdown -r now
Step 3: Re-check SELinux Status
When the system boots up, confirm the change by giving a sestatus command:
sestatus
How To Change Change SELinux Mode
Instead of disabling SELinux entirely, you change its mode to permissive. The actions that have been carried out leave a trace in the log file.
Now follow the steps below to switch the SELinux mode from enforcing to permissive type:
sudo setenforce 0
Now you should turn the enforcing mode on, so enter the command below:
sudo setenforce 1
These changes are only valid for the current session. They will return to their default values after a system reboot. To make those changes permanent, you should edit the configuration file using a text editor (like nano, for example).
Want a better way to host your websites and web apps? Developing something new? Simply don’t like Windows? That’s why we have Linux VPS. Linux Hosting Simplified
Linux Hosting Simplified
Securing your CentOS 7 Server Beyond SELinux
Now that you have installed SELinux on your CentOS 7, you can rest knowing your system is more secure than before. Of course, there is no way to ensure that any system is entirely secure. There is always more to be done — look, for example, at the items in this guide to securing your Linux VPS. In fact, even with SELinux, we have only used the most basic security measures it has to offer. More than that, whatever safeguards you establish will count for nothing if the hosting provider for your server isn’t secure enough. That is why, at Cloudzy, we maintain the highest levels of security, with hardware and AI-based firewalls, smart DDoS protection, and other proprietary measures. Enjoy our CentOS VPS solutions and run a truly secure server.