Cloud Computing Virtualization Technology abstracts physical servers into software-defined pools of compute, storage, and networking resources. It lets multiple tenants share the same hardware while keeping workloads isolated. This invisible layer drives agility in development and cuts resource waste to a fraction of traditional data centers.
Understanding how this engine works can transform budgets and delivery cycles. Many startups and established teams rely on virtualization to match on-premise costs with cloud flexibility. By breaking free of hardware cycles, IT groups deploy updates and spin down test environments in minutes instead of weeks.
What is Cloud Computing Virtualization Technology? Unveiling the Core Concept
At its essence, Cloud Computing Virtualization Technology creates an abstraction layer that separates workloads from the underlying hardware. Resource pooling becomes possible, so CPU, memory, and storage units combine into flexible buckets. Multi-tenant environments emerge, allowing isolated virtual machines and containers to run side by side on shared servers.
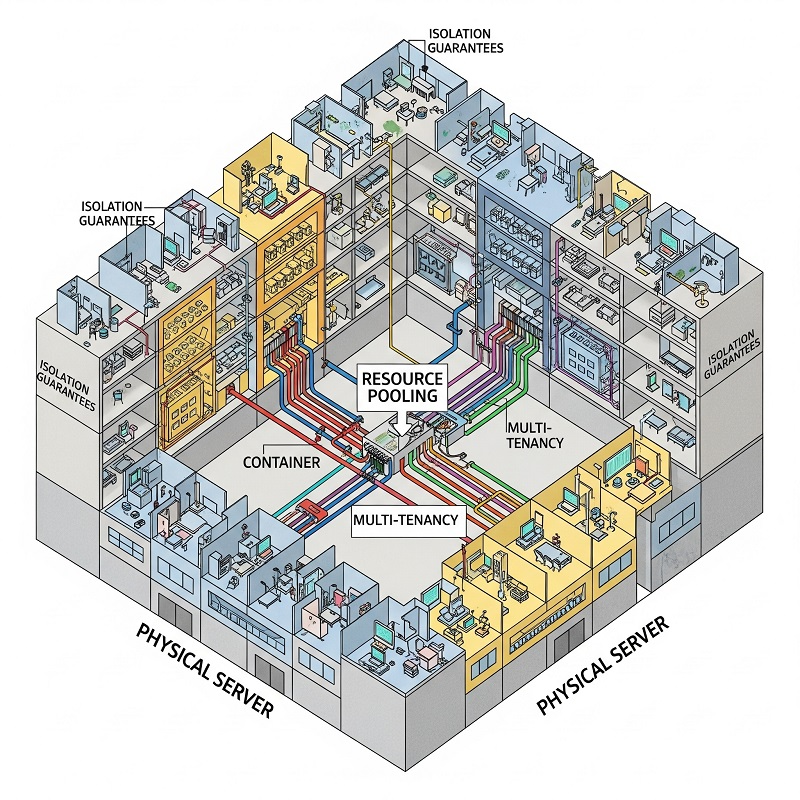
- Resource pooling: Physical assets convert into shared resource pools managed by software.
- Multi-tenancy: Multiple users host workloads on the same host without visibility into each other’s data.
- Isolation guarantees: Virtual boundaries protect each tenant’s environment from noisy neighbours.
This core concept underpins everything from on-demand scaling to cost-efficient test beds. Without it, elastic infrastructure would remain a distant goal.
How Cloud Computing Virtualization Technology Works: A Deep Dive into the Hypervisor Layer
Under the hood, virtualization hinges on hypervisors that carve physical servers into logical units. Those hypervisors sit between hardware and virtual machines, managing CPU scheduling, memory allocation, and I/O routing. Understanding each layer clarifies why performance and security depend on choosing the right software.
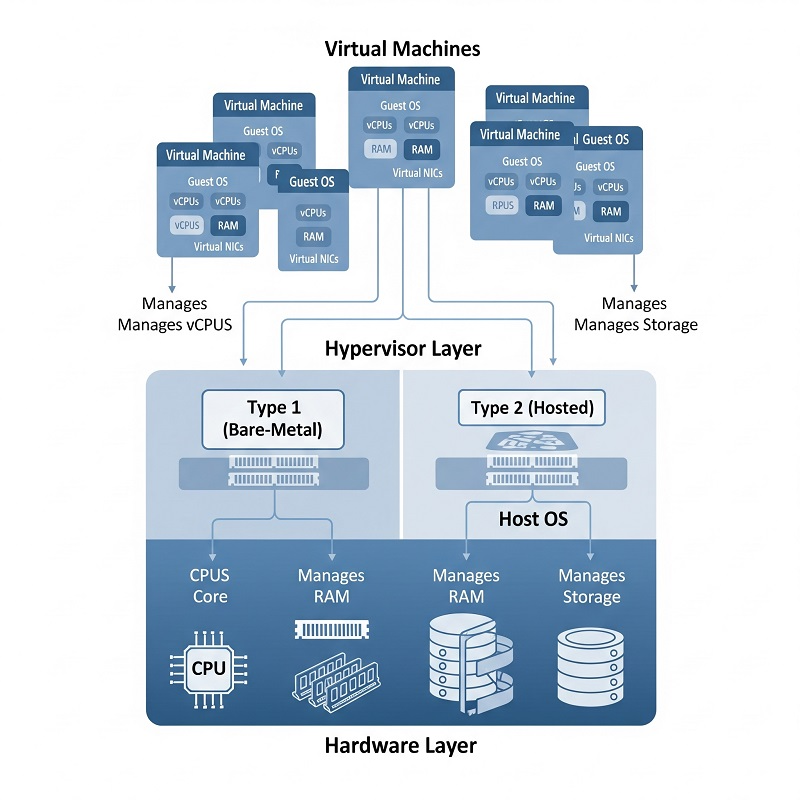
- Hardware layer:
- Multi-core CPUs
- RAM banks
- Network interfaces
- NVMe or SSD storage
- Hypervisor layer:
- Type 1 (bare-metal): Runs directly on hardware for lower overhead and tighter control.
- Type 2 (hosted): Lives atop a host OS, simplifying setup at the cost of extra latency.
- Virtual machines:
- Guest OS instances with configurable vCPUs, RAM, and virtual NICs
- Snapshots and live migration for flexible workload moves
By tuning hypervisors, operators balance resource overhead against direct hardware access. The right mix of Type 1 and Type 2 hypervisors determines how snappy and secure each VM will feel.
The Critical Importance of Cloud Computing Virtualization Technology in Modern IT
No cloud platform could scale to millions of instances without virtualization at its heart. That software layer opens up features that data centers of old could only imagine. Teams gain fine-grained control over capacity and recover from failures without forklift upgrades.
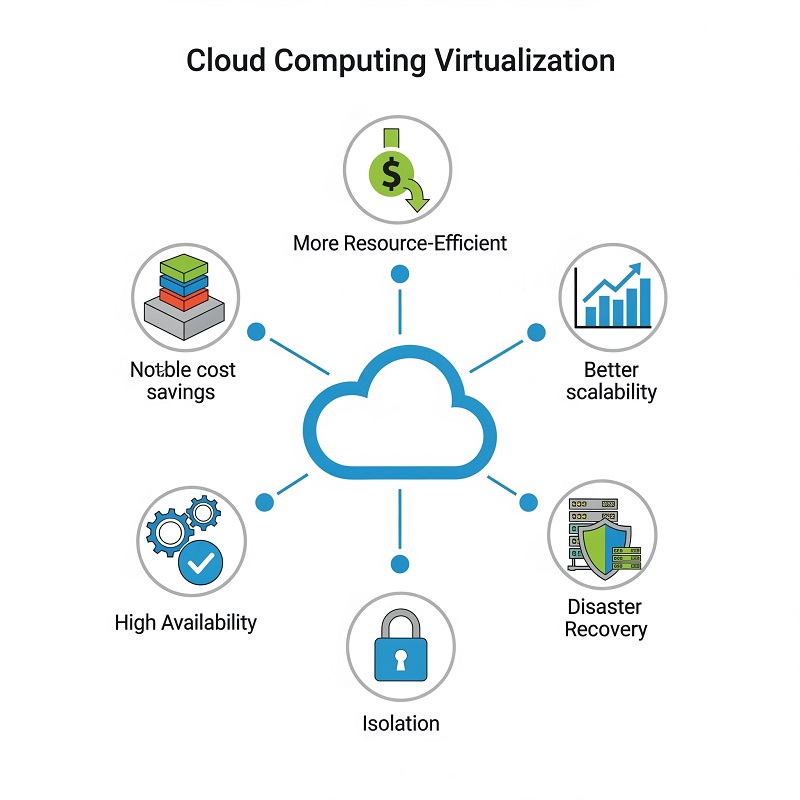
- More Resource-Efficient
- Notable cost savings
- Better scalability
- High Availability
- Isolation
- Disaster Recovery
Those six pillars let organizations move fast on proof-of-concept projects while still meeting production SLAs. Virtualization forms the foundation for hybrid designs that blend on-premise gear with public clouds.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing Virtualization Technology
Virtualization delivers clear, measurable advantages across every corner of your IT landscape, from squeezing extra cycles out of existing hardware to streamlining recovery strategies. By turning idle CPU cores and unused memory into on‑demand resources, it lets you reassign capacity instantly when demand spikes or outages strike. This flexibility means virtual workloads handle traffic surges and failover tests more smoothly than traditional bare‑metal servers, so you can focus on innovation instead of firefighting.
| Benefit | Explanation | ||
| High resource utilization | Idle CPU and memory reclaim for other VMs, boosting efficiency across hardware clusters. | Idle CPU and memory reclaim for other VMs, boosting efficiency across hardware clusters. | |
| Improved disaster recovery | Snapshot-based replication cuts recovery-time targets dramatically—compare DRaaS and VPS backup. | Snapshot-based replication cuts recovery-time targets dramatically—compare DRaaS and VPS backup. | |
| Speedier Deployments | New VMs spin up in seconds, slashing lead times for dev/test cycles. | ||
| Less Energy Drain | Consolidation means fewer racks, lower power bills, and reduced cooling requirements. | ||
| Better security through isolation | Virtual network controls and sandboxed environments tighten attack surfaces. | Virtual network controls and sandboxed environments tighten attack surfaces. |
Those upsides make virtualization a go-to for cloud-native architectures. Without it, any elastic service would grind to a halt under load.
Different Types of Cloud Computing Virtualization Technologies
Virtualization isn’t one-size-fits-all; it comes in flavors suited to servers, desktops, and networks. Server virtualization and desktop virtualization let you carve secure instances from the same hardware, while network and storage virtualization spin up flexible topologies and pooled disks on demand. Grasping each virtualization type steers architects toward tools that match performance requirements, security policies, and budget constraints.
| Technology Type | Description |
| Server Virtualization | Abstracts physical servers into multiple VMs with dedicated slices of CPU and RAM. |
| Desktop Virtualization | Delivers full OS sessions to user devices over the network—also known as VDI. |
| Application Virtualization | Runs specific apps in isolated containers without full desktop overhead. |
| Network Virtualization | Defines software-based networks and routers for flexible traffic steering. |
| Storage Virtualization | Pools multiple storage arrays into unified logical volumes. |
| Data Virtualization | Creates abstract data layers without moving or copying underlying data sources. |
| Operating System Virtualization | Uses container engines like Docker or Kubernetes for lightweight isolation. |
| Hardware Virtualization | Relies on CPU extensions (Intel VT-x, AMD-V) to accelerate VM operations. |
| GPU Virtualization | Shares GPU cores across multiple VMs for parallel compute tasks. |
| Data Center Virtualization | Integrates compute, network, and storage into unified resource domains across racks or rooms. |
Those approaches combine to form the modular building blocks of public clouds and private infrastructures alike. Picking the right mix can smooth migration paths and cut compatibility headaches.
Implementing Cloud Computing Virtualization Technology: Key Considerations
Rolling out virtualization requires more than software installs; it calls for planning around hardware lifecycles, costs, and security rules. Small oversights can lead to bottlenecks or audit headaches down the line.
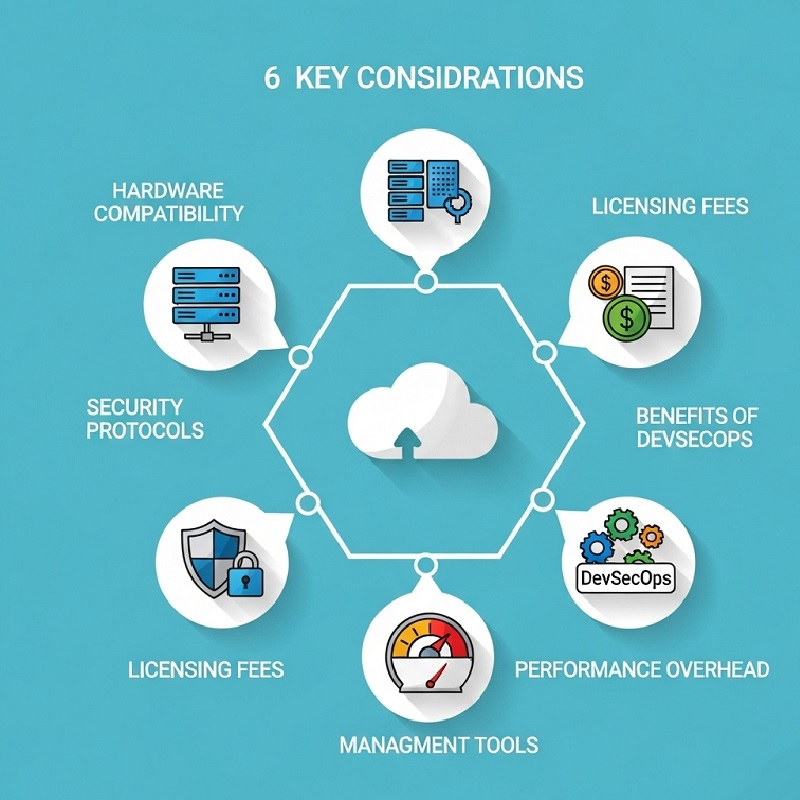
- Hardware Compatibility: Match server firmware and CPU feature sets before deploying hypervisors.
- Licensing Fees: Factor in costs for proprietary hypervisor suites or container orchestration licenses.
- Security Protocols: Use cloud access management to control who can spin up or tear down VMs.
- Benefits of devsecops: Integrate security and compliance scans directly into CI/CD pipelines to catch misconfigurations before they reach production.
- Performance Overhead: Measure I/O and CPU tax introduced by each virtualization layer.
- Management Tools: Centralize logs, metrics, and orchestration through platforms like OpenStack or vSphere.
Addressing those five areas keeps your virtualization rollout from slipping off schedule. Proper upfront checks pay dividends as scale and complexity grow.
Drawbacks, Challenges, and Risks of Cloud Computing Virtualization Technology
Virtualization delivers efficiency and flexibility, but it also adds complexity you can’t ignore. If you skip configuration checks or lag on hypervisor updates, you may see odd slowdowns and find unexpected security holes. Running planned health checks and routine patch cycles helps keep those issues from causing trouble.
- Performance Overheads: VM context switches and I/O virtualization add latency.
- Complex Management: Multiple layers require specialized skills to stitch together effectively.
- Single Point of Failure: A compromised hypervisor can jeopardize all hosted VMs.
- Security Issues: Hypervisor vulnerabilities open the door to cross-VM attacks.
- Resource Contention: Heavy workloads on one VM can starve its neighbors.
- Backup and Recovery Differences: VM-aware tools differ from physical backups in handling snapshots.
- Compliance Complexities: Virtual audit trails must track both hypervisor and guest activities.
- VM Sprawl: Without governance, inactive VMs accumulate and waste licenses.
- Data Leakage Risks: Misconfigured virtual networks can expose sensitive flows.
- Incompatibility Issues: Some legacy software may not run well inside VMs.
By mapping out those risks and assigning responsibilities, IT teams keep virtualization from becoming a hidden liability. Ongoing reviews and fine-tuning safeguard both performance and security.
Cloudzy VPS: Practical Application of Cloud Computing Virtualization Technology for High-Performance Hosting
Cloudzy’s VPS lineup showcases how virtualization delivers dedicated-like performance on shared infrastructure. By slicing NVMe-backed servers into virtual instances, each box feels as exclusive as a physical host. With API-driven provisioning, instant scaling, and multiple payment options, teams can buy VPS plans that align with project timelines without heavy procurement cycles.
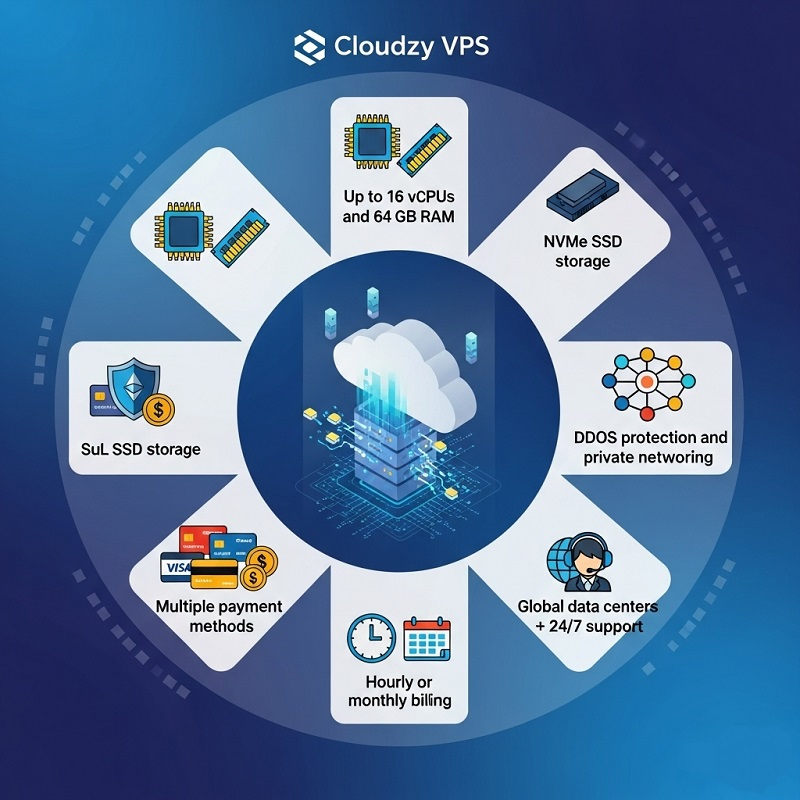
- Up to 16 vCPUs and 64 GB RAM per instance for compute-heavy workloads.
- NVMe SSD storage delivering sub-millisecond I/O latency for database apps.
- DDoS protection and private networking options for hardened isolation.
- Multiple payment methods, including credit card, PayPal, Bitcoin, and Alipay, for seamless transactions.
- Hourly or monthly billing in multiple currencies without long-term commitments.
- Global data centers plus 24/7 support for mission-critical deployments.
Those cloud-based server features mean you get the agility of public clouds with the control of private racks. Opting to buy a VPS with Cloudzy delivers both high performance and cost predictability, without hidden fees or complex contracts.
Conclusion: Virtualization—the Undeniable Core of Cloud Computing’s Future
Virtualization often flies under the radar, but it’s the engine that keeps modern IT humming. By reclaiming unused CPU cycles and connecting on‑premise setups with cloud services, it lets teams move fast without worrying about hardware procurement. Mastering these invisible layers means rolling out new features with confidence and leaving capacity headaches behind.
When teams balance different hosting options—from shared platforms to isolated VPS—virtualization remains the invisible linchpin keeping everything running smoothly. As companies weigh saas vs. self-hosting, they’ll find that the same core virtualization layers power each choice.
It turns raw hardware into adaptable pools you can configure on demand, so performance stays consistent even under unpredictable loads. As orchestration tools evolve, those software‑defined layers will handle more complex workflows with less manual intervention and lower operational risk.




One thought on “Cloud Computing Virtualization Technology: The Invisible Powerhouse of Modern IT”
Great breakdown of how virtualization underpins modern cloud infrastructure. One aspect I’d love to see explored further is how different types of hypervisors (like Type 1 vs Type 2) impact performance and scalability in cloud environments. That could add even more depth for readers trying to understand what’s going on behind the scenes.