Before diving into the basics and key points of QEMU vs KVM, let’s start with a burning question that may be poking at your brain. What is the big thing about Virtualization software?
Here’s a simple answer without getting super technical; High-level IT management and execution.
Virtualization software is hot right now, and for a good reason. Virtual technology can be your best friend whether you are a full-time trader, gamer, programmer, or business owner. If you care about improving IT agility, flexibility, and scalability and are looking for cost-effective virtualization software, read this QEMU vs KVM article until the end and keep a look out for our special VPS offer; it’s a good one.
What Is a Hypervisor?
Before discussing “what is KVM?” And “what is QEMU?”, we should go through the definition of a hypervisor. A hypervisor is a technical process that creates a divider between the host’s hardware components and a computer’s operating system.
There are type-1 and type-2 hypervisors that function differently. Type-1 hypervisor, mostly known as a bare-metal hypervisor, is in charge of executing commands on the host’s hardware. Type-2 hypervisor, known as a hosted hypervisor, creates virtual environments on multiple devices while running on a conventional operating system.
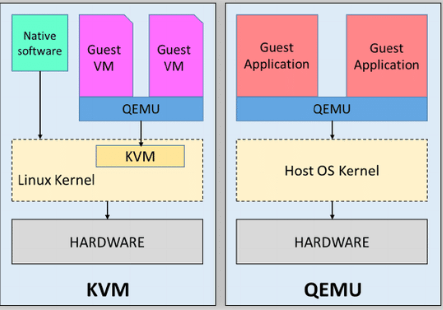
What is QEMU?
QEMU is short for Quick Emulator and is open-source virtualization software that can emulate CPUs and hardware. In other words, you can use QEMU to run operating systems and applications that are not compatible with your host operating system hardware platform. So, to answer the question “What is QEMU?” in simple words, it’s basically a hardware virtualization tool that can enhance your virtual machine performance. For example, if you have an x86-based Linux computer, QEMU can successfully help you run ARM software (which is incompatible with your x86 hardware).
Since QEMU emulates a full system, you can use it to run different operating systems without having to reboot your computer. To give you an initial sneak peek into QEMU vs KVM’s highlights, QEMU runs on both Windows and Linux, but KVM runs only on Linux-based host OS.
What is KVM?
KVM is short for Kernel-based Virtual Machine that turns your Linux system into a type-1 (bare-metal) hypervisor. KVM allows you to create isolated virtual environments, and since it’s built into Linux operating system code, it has all the features that come with the Linux kernel. To enjoy the ultimate KVM experience, implement it on a supported Linux distribution, such as Ubuntu or CentOS.
 Linux Hosting Simplified
Linux Hosting Simplified
Want a better way to host your websites and web apps? Developing something new? Simply don’t like Windows? That’s why we have Linux VPS.
Get your Linux VPSQEMU Vs KVM; What is Their Main Difference?
When it comes to KVM vs QEMU, you need to know that KVM acts as an outer guard that monitors QEMU executions to make sure the performance level is at its highest. But how does KVM enhance performance, you may ask? Imagine you partition the CPU to make a virtual CPU for your virtual environment. By providing hardware-assisted virtualization, KVM allows mapping between the vCPU and the actual CPU. This way, all the tasks that are delegated to vCPU get executed on one tiny slice of the physical CPU. KVM runs as a Linux kernel module. That’s how it can offer hardware-assisted virtualization and not sacrifice performance.
Although These tools are pretty similar in what they do as the end result, if you want to choose one for the long run, you need to learn about their unique features, and that means it’s time for the ultimate comparison table.

KVM is a type-1 hypervisor, and QEMU is a type-2 hypervisor. That is the main difference between QEMU and KVM, but if you want to choose one for the long run, you need to learn about their unique features, and that means it’s time for the ultimate comparison table.
QEMU Vs KVM; The Ultimate Comparison Table for 2022
The best way to decide between QEMU vs KVM is to examine them separately. However, since KVM is a type-1 hypervisor, it can act as a fully independent virtual solution and might be a better option. One key point about QEMU is that it executes all commands without depending on your hardware. That means QEMU is translating between processors frequently, resulting in very slow performance. But if you enable KVM and then use QEMU, your virtual experience speeds up significantly.
To spot the difference between QEMU and KVM, it is best to look at specific features of KVM vs QEMU.
| Feature/Technology | QEMU | KVM |
| Operating system | Linux, Microsoft Windows, macOS and some other UNIX platforms | Linux, macOS and some other UNIX platforms |
| Open-source and free | ✔ | ✔ |
| Supports multiple disk image formats | ✔ | ✖ |
| Live migration | Can be done through a complicated process | ✔ |
| Executing multiple virtual CPUs in parallel | ✔ | Yes, depending on the load limits of guest virtual machines |
| Integration with Different VM Solutions | Yes, including VirtualBox, Xen-HVM, Win4Lin Pro Desktop | Limited to a maximum of 4 virtualized (emulated) IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) devices per guest virtual machine |
| Running Docker instances | Cannot be done in most cases | ✔ |
| Dynamic memory management | ✖ | ✔ |
| Virtual hardware support | Limited | ✔ |
| Native GUI | Limited | Limited |
| Multipath I/O | Supported | Supported |
| Memory management | User-mode memory | Includes memory management features of Linux |
| Low latency | Higher compared to KVM | ✔ |
| 32-bit and 64-bit processors | Supported | Supported |
| Minimum RAM for configuring the host OS | 1 GB | 1 GB |
| SMP hosts | Supported | Supported |
| SMP guests | Supported up to 255 CPUs | Supported up to 16 CPUs |
Advantages of KVM Vs QEMU Virtualization
With all the hot talk about virtual machines, more and more people are eager to learn about the actual benefits of virtualization software, which could take their business, trading, gaming, etc., to a higher level. So let’s go over some of the KVM vs QEMU advantages.
-
Use of hardware resources on a software level
Since virtual machines use physical resources in most cases, the guest OS can use physical hardware, such as host memory, CPUs, or storage space, freely and more efficiently.
-
Configuration control
You can configure virtual machines directly from the host, which means you have software-level control over the configuration process.
-
Host OS stability and security
Virtualized kernels are separate from the host operating system. Since a guest operating system runs on virtualized kernels, your host OS’s stability and security are protected should your guest OS encounter failures.
-
Budget-friendly
Physical servers cost a fortune, and you cannot risk your entire budget only to learn you could have invested in a far superior option; virtualization software. The best thing about VM is that it cuts all the maintenance costs that will inevitably accompany even the best physical server.
-
Free and open-source
Using open-source software can be a huge plus for optimizing telecommunication systems, inventory, accounting, personal productivity applications, contact management, and operating systems. Open-source software offers reduced hardware costs, integrated management, license management, scalability, and many other benefits.
KVM Vs QEMU, When to Choose Which?
Although in this blog post, we’ve mentioned the high potential of using KVM and QEMU combined, it’s noteworthy to keep in mind that these tools have specific purposes. Choosing KVM is a wise decision when you need to run multiple virtual machines on one physical server since it allows you to take advantage of several VMs working in parallel while keeping the performance at its high.
QEMU, on the other hand, is a machine emulator that is able to emulate various hardware architectures and run guest operating systems that are different from the host’s architecture. So, it can be an independent tool for system emulation.
KVM/QEMU VPS Hosting; The Solution to All Your Security and Performance Problems
Implementing KVM technology in making virtual servers results in virtual private servers that beat any similar service regarding performance. As the most efficient virtualization method, KVM integrates with the server’s infrastructure seamlessly, fetching exceptional performance and functionality.
In terms of security, KVM takes full advantage of virtualization to isolate the VM even more. This way, you’re promised built-in security.
At Cloudzy, we’ve chosen KVM as our primary virtualization method to enhance the performance and security of our servers. On top of that, we’ve added another impenetrable layer of security: AI-powered DDoS protection. In simple words, our KVM VPSs are double-guarded. Pre-installed OS, full admin and root access, 7-day money-back guarantee, 99.95% uptime, and 24/7 support are among other top-end features we offer on our KVM VPS plans. So, if you’re looking for a server that’s both highly secure and performant, take a look at our KVM VPS plans.
Final Words
Many factors come into play when deciding to invest in virtualization software, especially if it’s a tight competition like KVM vs QEMU. However, what’s most important is to pick software that can serve you best. We suggest using both KVM and QEMU to get all the benefits in one package, but if your current budget forces you to pick one, KVM provides a powerful virtualization experience all on its own.
You can take advantage of our special VPS offer and enjoy all the benefits of KVM at the best possible rate. One smart decision can put you five steps ahead, and with our cost-effective VPS services, you can experience virtual machines at a whole new level.
FAQ
KVM vs QEMU; which is faster?
KVM is faster, but this is not the only feature you should consider. The best virtualization solution is fast, secure, reliable, scalable, and cost-effective. If you are looking for the perfect virtualization package for your VM, we suggest using them both.
Is QEMU required for KVM?
KVM is a Linux-based full virtualization solution, so you can definitely use it without QEMU. However, if you are looking for a powerful type-1 hypervisor that provides better performance and stability, using KVM and QEMU together is your best bet.
Which operating systems can I use with KVM?
Aside from Linux, KVM supports various popular operating systems, including BSD, Solaris, Windows, Haiku, ReactOS, Plan 9, AROS Research Operating System, and macOS. Note that you can install Windows as a guest OS on KVM.
Can QEMU work without KVM?
Yes. KVM and QEMU are entirely independent of each other. However, if you use KVM to run QEMU, you won’t have to worry about execution failures on the host CPU.
Is QEMU a hypervisor?
QEMU is a type-2 hypervisor (hosted hypervisor) that can create multiple virtual environments while emulating essential hardware components such as video cards, disk controllers, network cards, etc.
Is QEMU secure?
QEMU executes commands from a guest CPU, which means it is vulnerable to malicious attacks. So if you want to take security precautions, make sure you run QEMU in a restricted environment so that it can only access the required resources for running the virtual machine.





One thought on “QEMU vs. KVM: Exploring the Virtualization Giants”
I discovered QEMU some years ago, and have had a lot of fun getting old versions of Windows, various Linux LiveCDs, etc. to boot under it on Windows XP, Windows 10, and Linux Mint.
Unfortunately, I haven’t been able to get it to do most of what I want to do, because it is gawdawful complex and poorly dopcumented. Yeah, yeah, if you know the intimate innards of PC hardware — busses, protocols, general architecture — I’m sure you have no problem. But for somebody like me whose last foray into hardware was around 2001 and ended poorly, well, you could be doing a LOT BETTER.
Of greatest annoyance– no, that’s weak; it’s not annoyance, it’s PAIN! — is the observation that the 64-bit version of QEMU (specifically, qemu-system-i386.exe v 8.2.0) I installed a year or two ago under Windows 10, incurs an instruction exception of some sort partway through the installation of Windows 98, which Reddit indicates people also experience under VMware. Fortunately, the 32-bit version of qemu-system-i386.exe v 0.15.92) des NOT incur that problem, given EXACTLY the same launch command. Clearly, something in the default characteristics of an instance of qemu-system-i386 launched with a minimal command line, have changed between those two versions, but I have no idea WHAT, or what I might specify on the command line to make v 8.2.0 “look/act like” v 0.15.92 in this important respect. It would be nice to be able to use the “latest and greatest,” QEMU for the things I need/want to do, but right now that’s not possible and I have to keep the old version around in order to do certain things like this.
Thanks in advance for any light you can shed.