Webmin is a great option if you are looking for an easy-to-use
interface for managing your VPS. Let’s see how to install Webmin on a
VPS.
Step 1: Install
Dependency Packages
First, you need to install the dependency packages. Enter the
following command in your terminal.
sudo yum install nano -yStep
2: Add the Webmin Repository to the Repository List
Open a terminal and enter the following command to add the Webmin
repository:
sudo nano /etc/yum.repos.d/webmin.repoStep 3: Write in the New
File
Add the following lines to the opened file:
[Webmin]
name=Webmin Distribution Neutral
#baseurl=http://download.webmin.com/download/yum
mirrorlist=http://download.webmin.com/download/yum/mirrorlist
enabled=1Step 4:
Download and Install the GPG Key
Now, you need to download and install the GPG key by using the
following command:
wget http://www.webmin.com/jcameron-key.ascsudo rpm --import jcameron-key.ascStep 5: Update the
Repository
Type in this command to update the repository:
sudo yum check-updateStep 6: Install
Webmin
Now, enter the following command to install Webmin:
sudo yum install webmin -yIf installation fails because the dependencies are not ready, just
re-enter the installation command.
Step 7: Start the
Service
To start the service and make it start automatically, use this
command:
chkconfig webmin onservice webmin startStep 8:
Change Firewall Settings to Allow Webmin
If you have a firewall, you should enable Webmin through the firewall
by entering the following command:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10000/tcpfirewall-cmd --reloadStep 9: Log in to
Webmin
Now, you can log in to Webmin. Open the following website in your
browser:
https://your-ip-addres:10000Step 10: Enter
Username and Password
Then, Enter your username and password by using the HTTPS protocol.
By default, the username is root, and the password is the root user’s
password.
Step 11: Configure your
VPS
Now, it’s time to configure your VPS with Webmin by going to
Webmin configuration.
Step 12: Change the
Standard Port
If your Webmin VPS has a public IP, go to ports and
addresses and put the standard port on
some.
Here you go. Now you know how to install Webmin on a VPS.
If you want to change your Webmin password, you can enter this
command:
/usr/libexec/webmin/changepass.pl /etc/webmin root NEWPASSWORDBut changing the password for a specific user for Webmin is not
recommended.
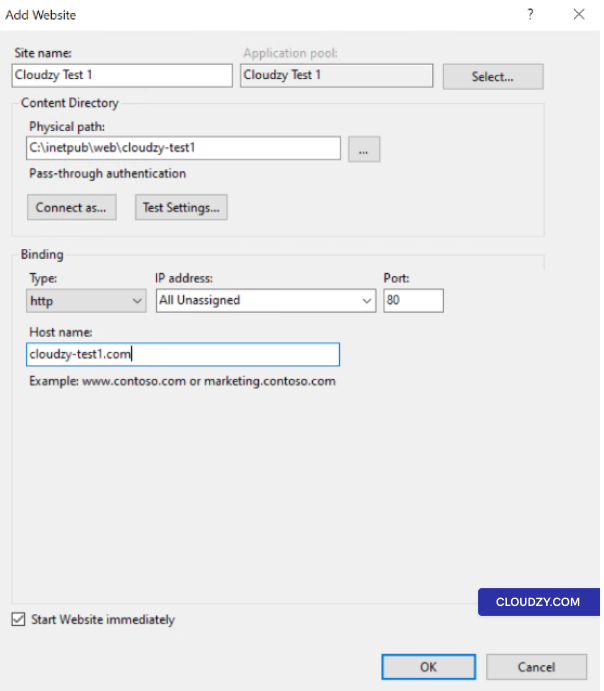
Webmin Virtual Host
One of Webmin’s many features is the Webmin virtual host. This allows
you to host multiple websites on a single server. After you install
Webmin on a VPS, you can create virtual hosts by following these
steps:
Step 1: Go to the control
panel.
Step 2: Update your Webmin to ensure you use its
latest version.
Step 3: Log in to Webmin and click on the
Servers icon.
Step 4: Click on Apache
WebServer.
Step 5: Select any address in the
Create a New Virtual Server part.
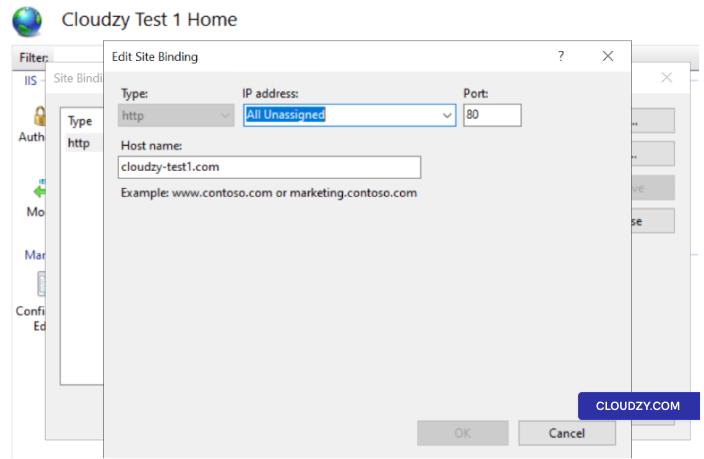
Step 6: In the port section, enter
80, and choose the last radio button.
Step 7: In the document root
section, put the name of the HTML files your virtual host will be.
Step 8: Enter the domain name in the server
name section.
Now, you’ve created the Webmin virtual host.
How
to Install Webmin on an Ubuntu Server or Debian-Based
Server
In the first section, we discussed installing Webmin on a REHL-based
VPS. Now, we will show you how to install Webmin on an Ubuntu or
Debian-based server.
First, you need to install the dependency packages by typing the
following command:
sudo apt install software-properties-common apt-transport-https -yAdd the Webmin repository and the GPG
key.
sudo wget -q http://www.webmin.com/jcameron-key.asc -O- | sudo apt-key add -sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] http://download.webmin.com/download/repository sarge contrib"Finally, install Webmin:
sudo apt install webmin -yIf you have a firewall, you should allow it by using this
command:
sudo ufw allow 10000/tcpThat’s it! You successfully installed Webmin on your server. The
default username is root, and the password is your
current root password.
Now, you need to open your web browser and navigate to the following
address:
Sometimes Debian or Ubuntu distributions do not allow users to log in
by the root user and its pass. In that case, you must
enter sudo for the username.
After you log in, you can configure your web server according to your
needs and goals.
Perfect! You now know how to install Webmin on your Linux VPS. If you
have any questions, don’t hesitate to contact us by submitting a
ticket.

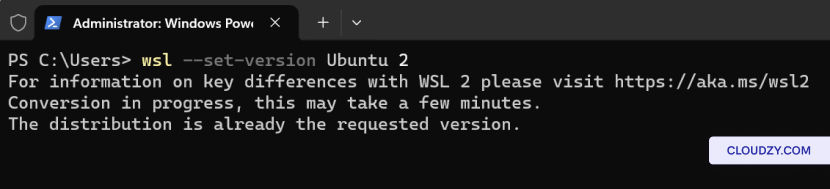
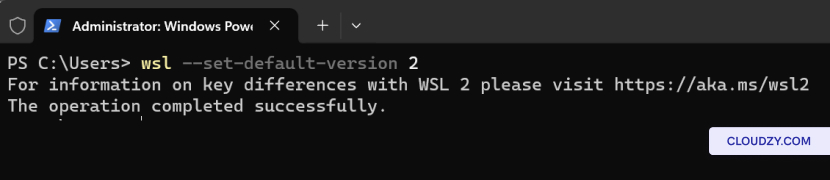
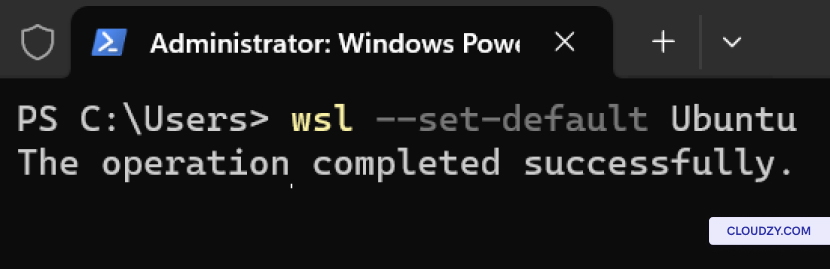
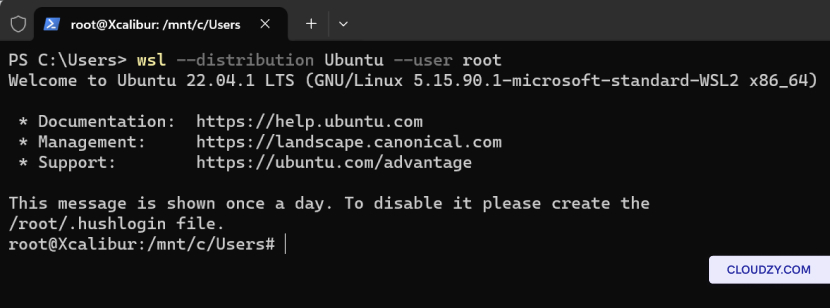

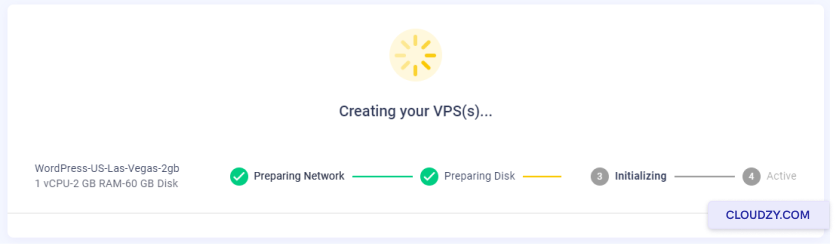
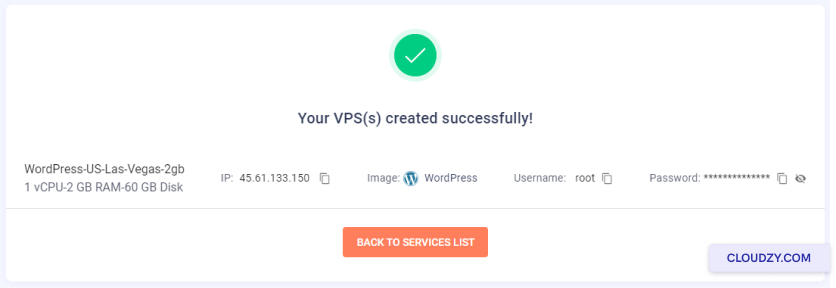
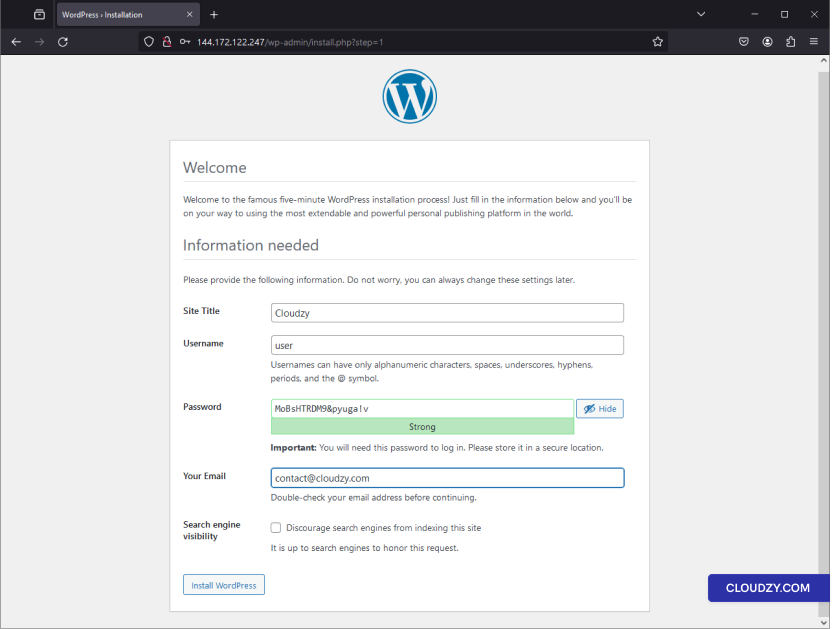
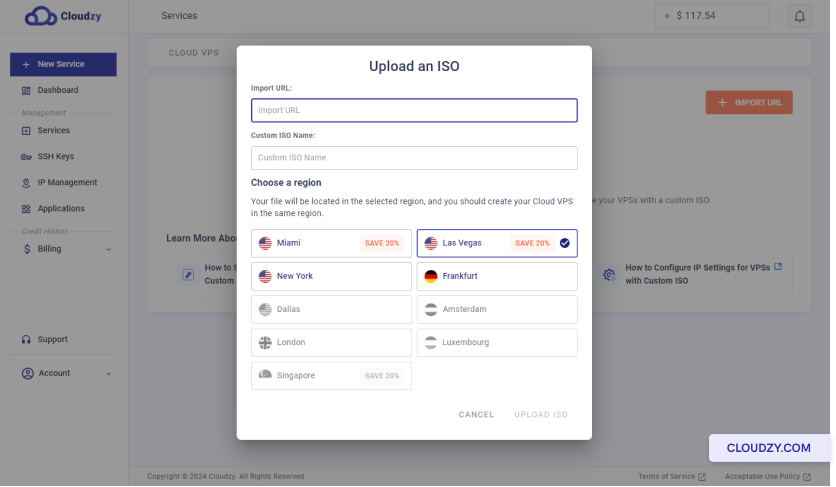
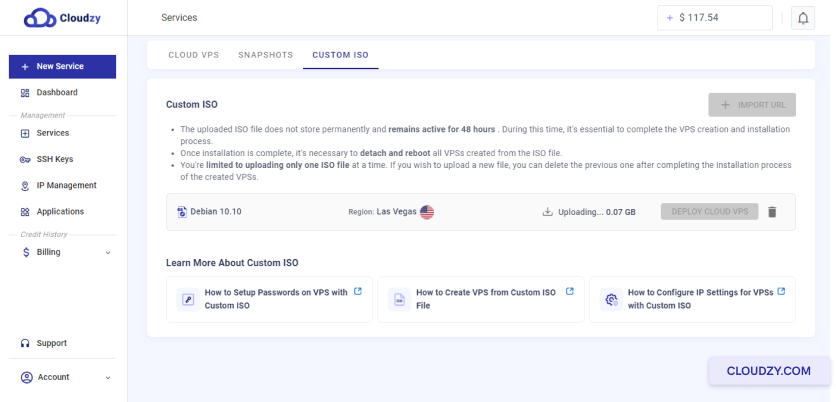
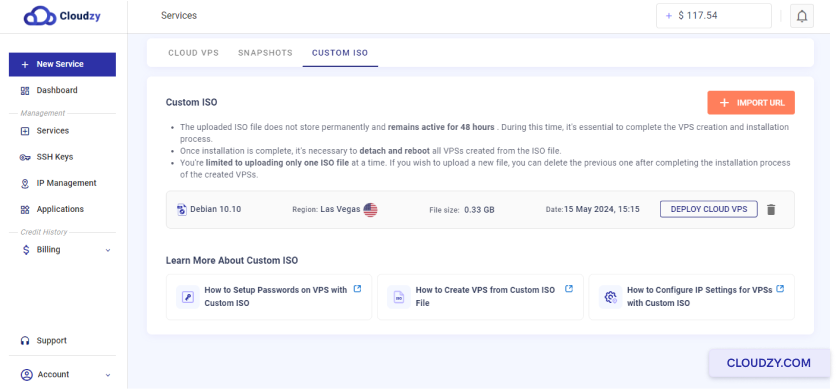
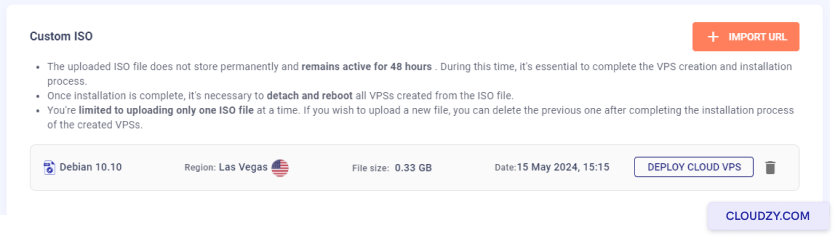
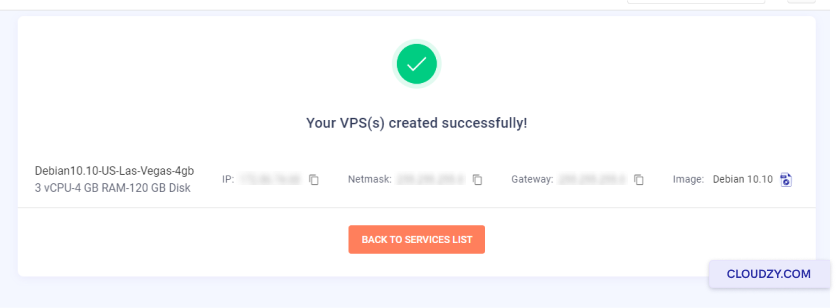
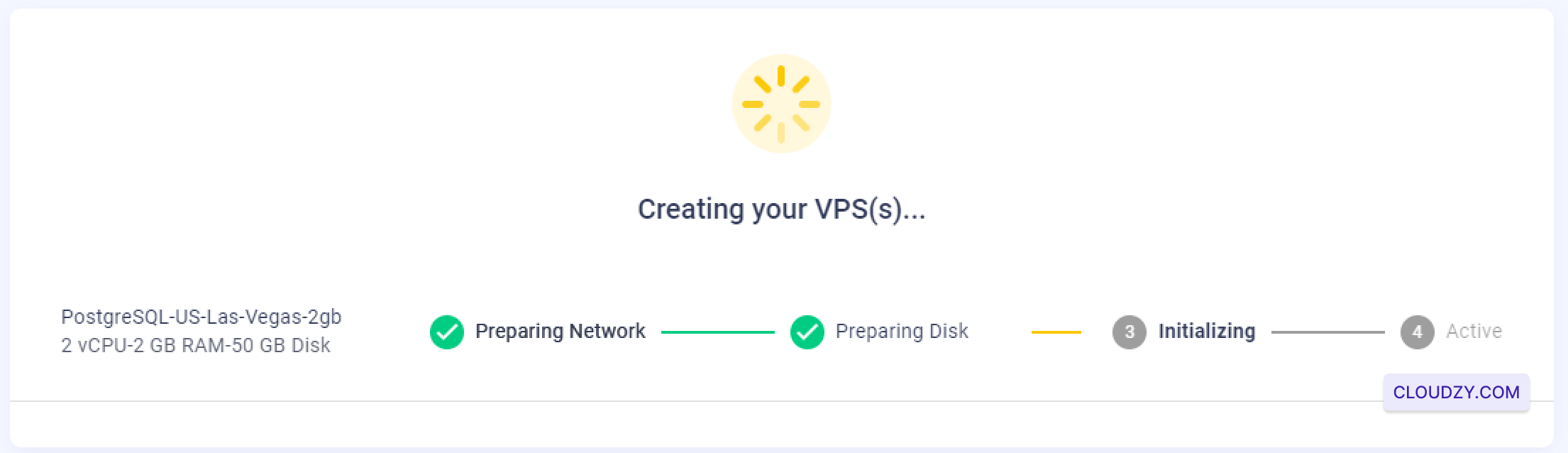
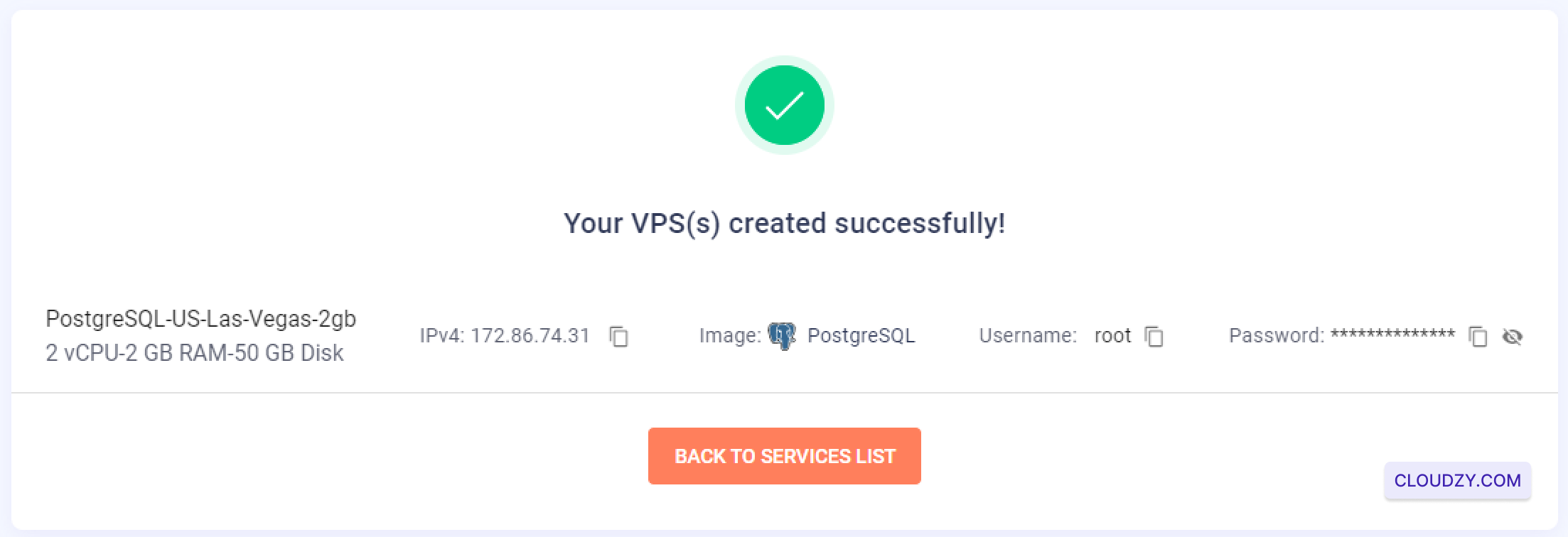
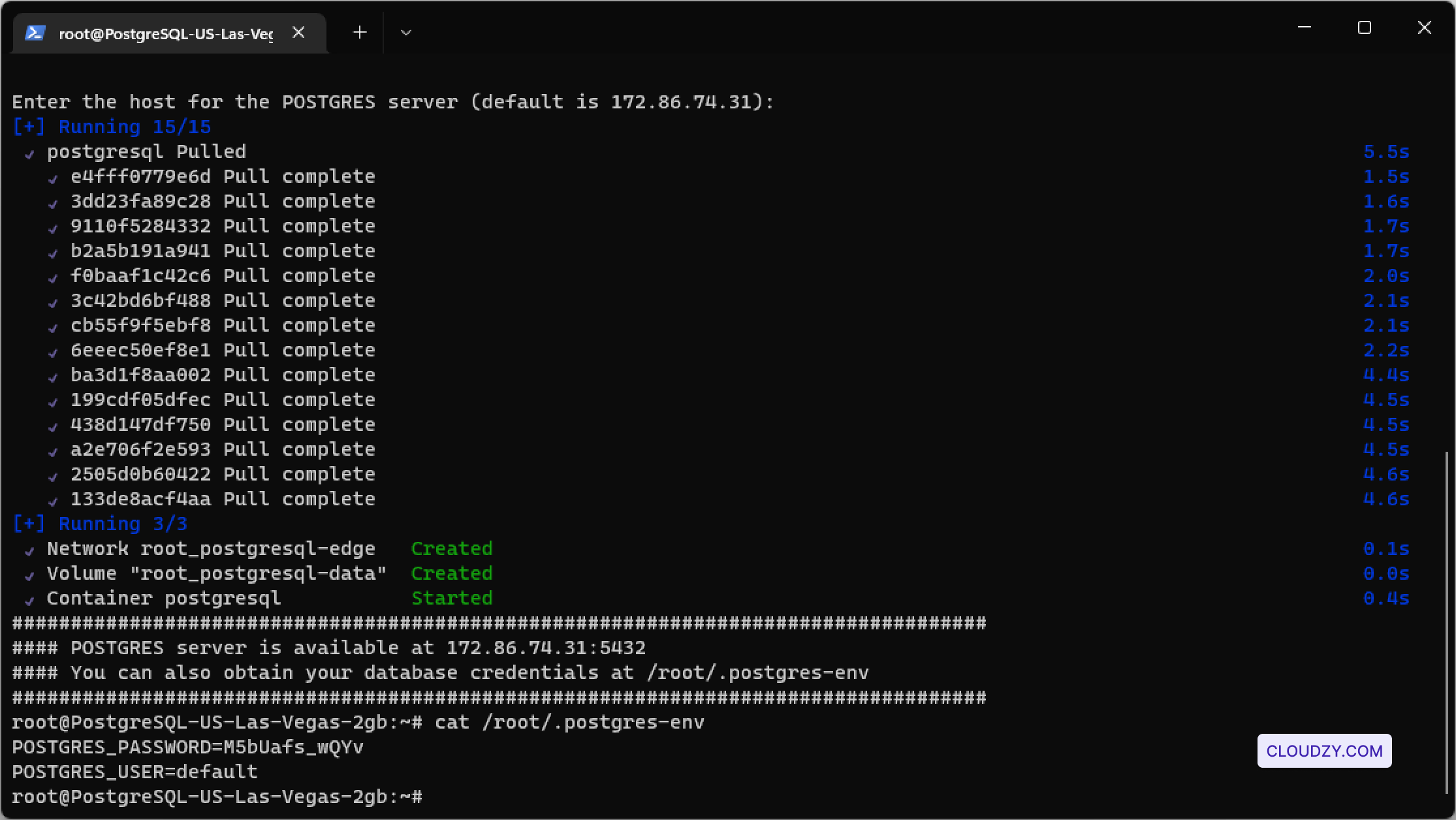

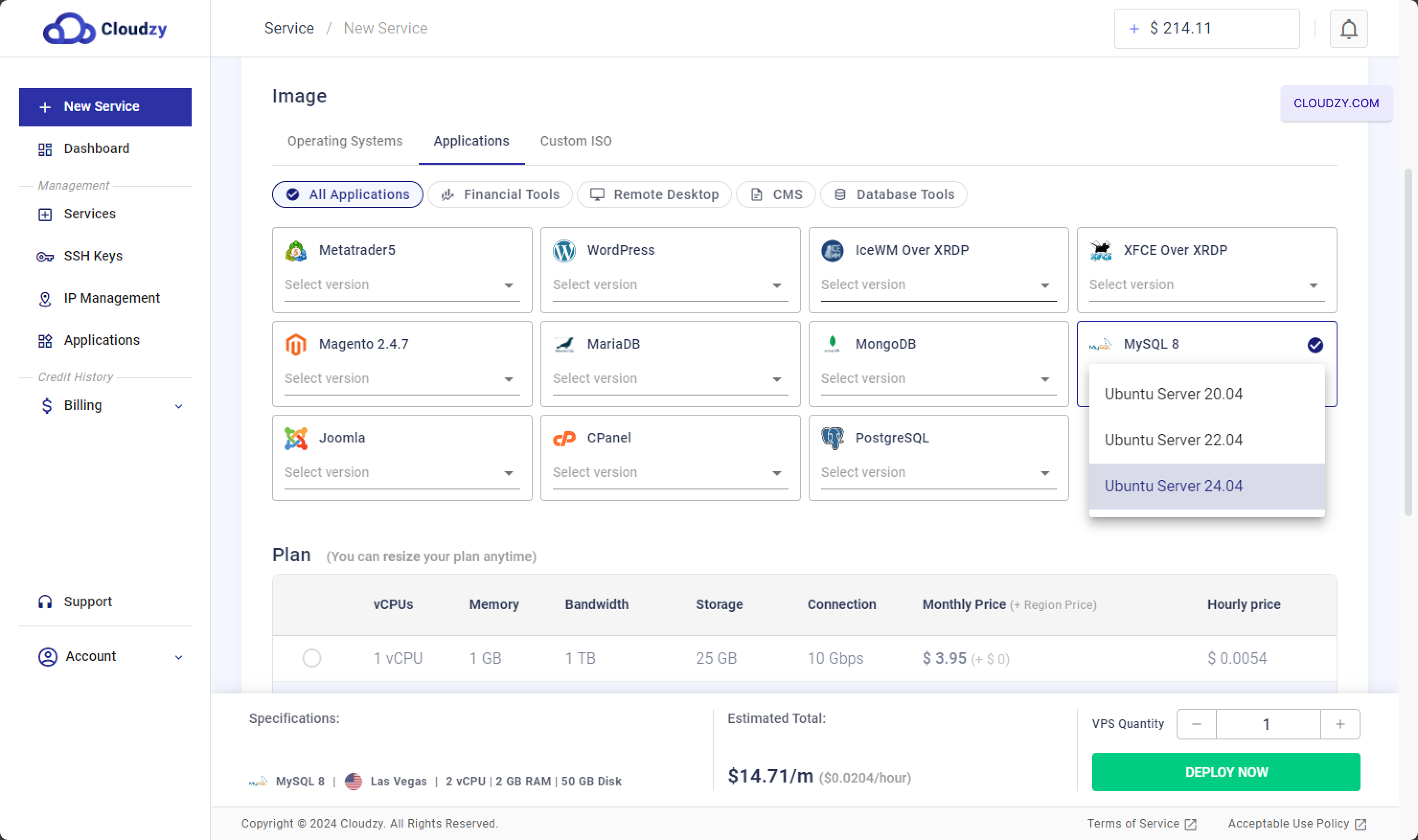
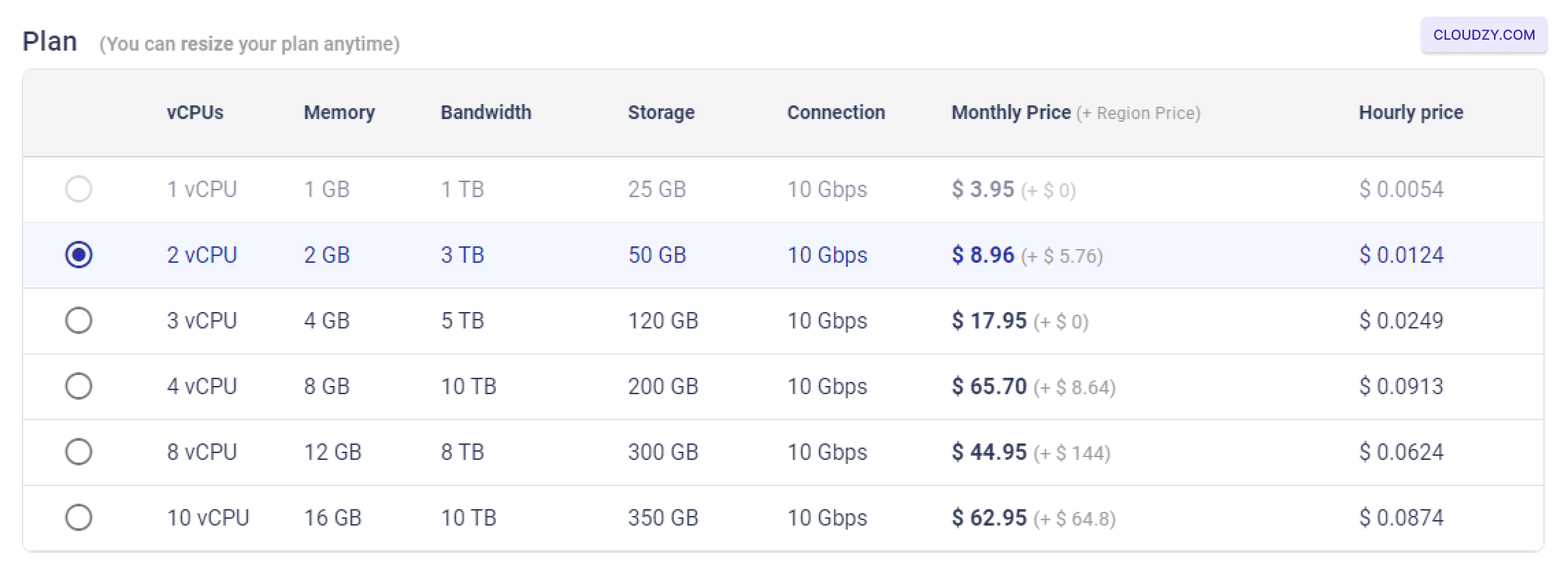


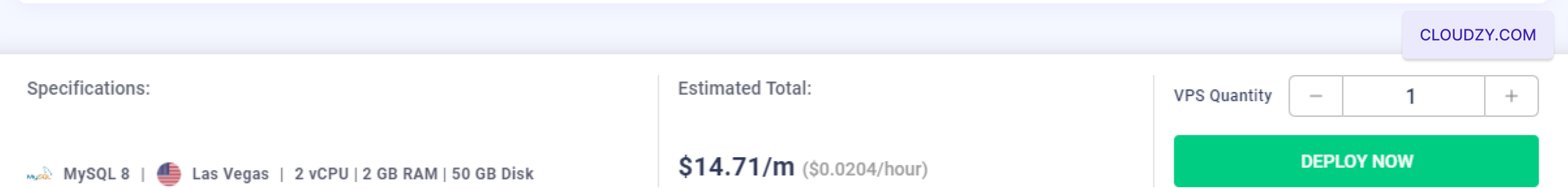
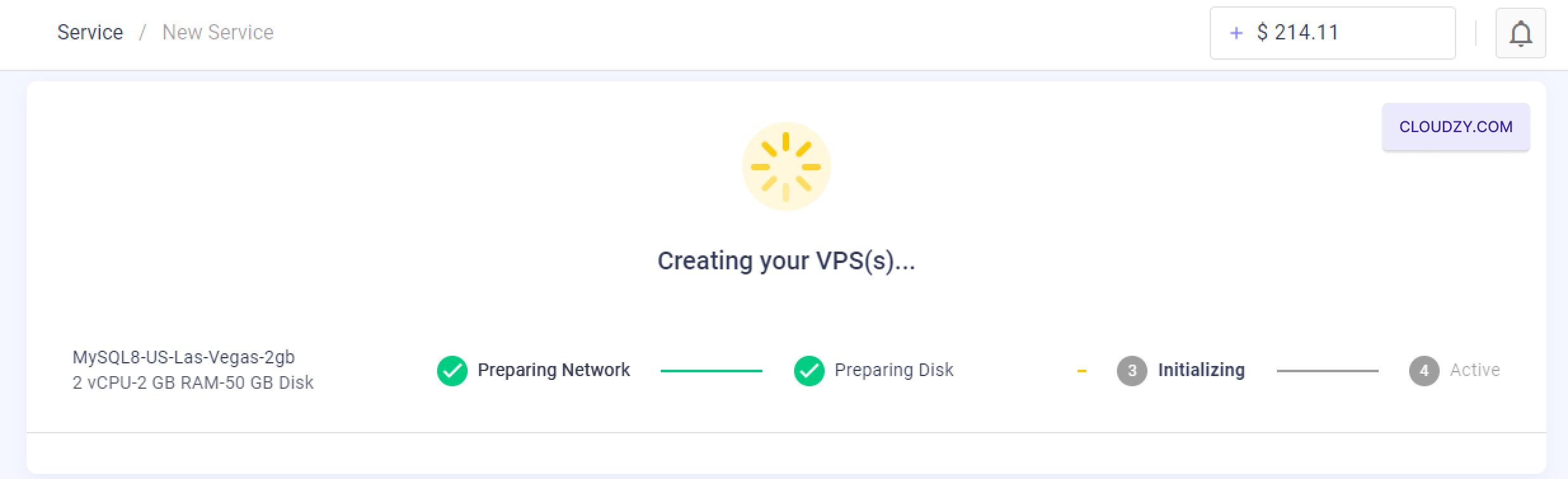
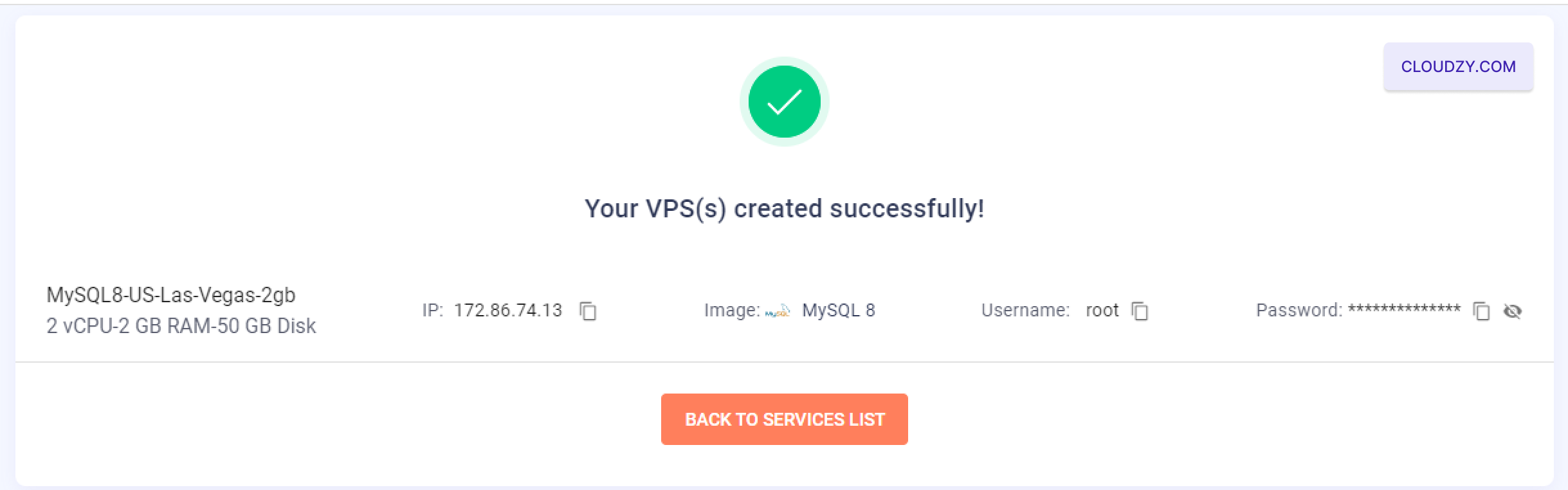
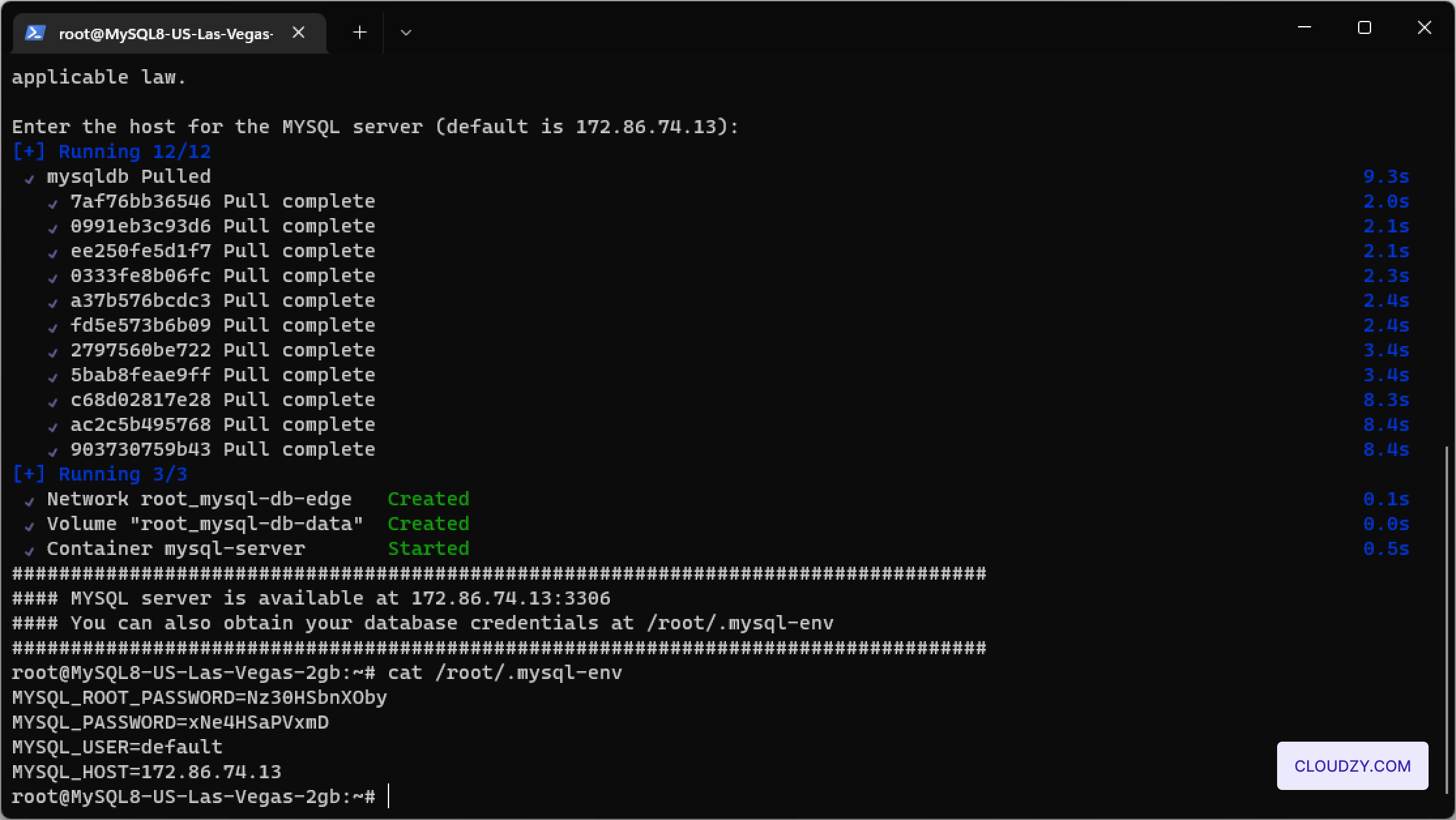




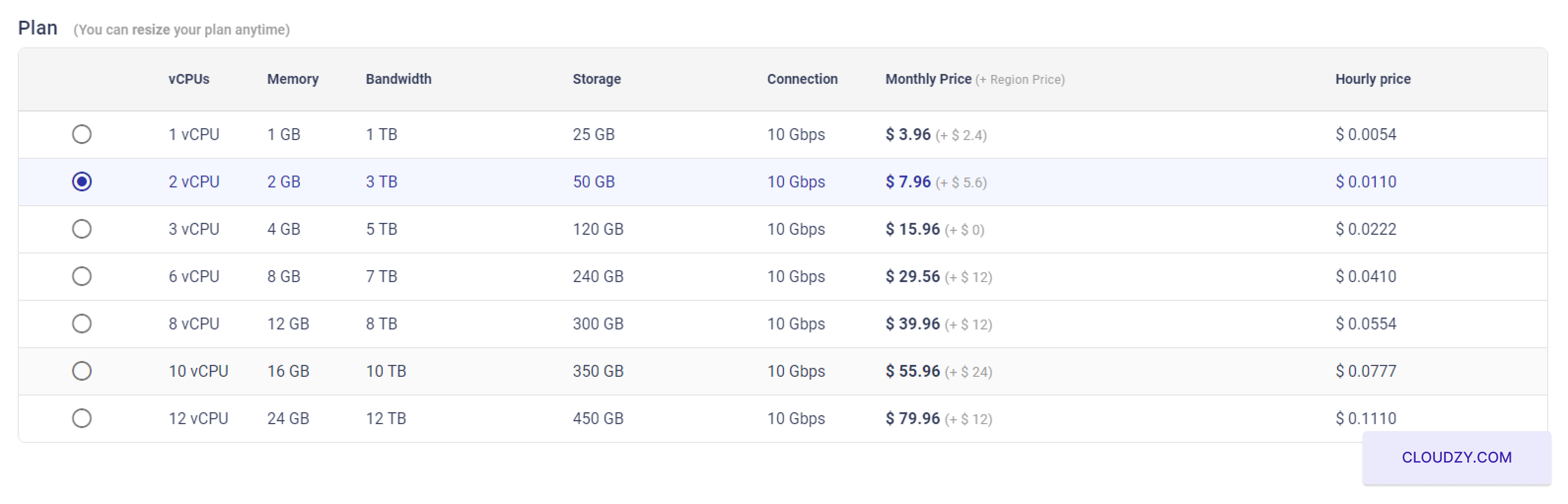
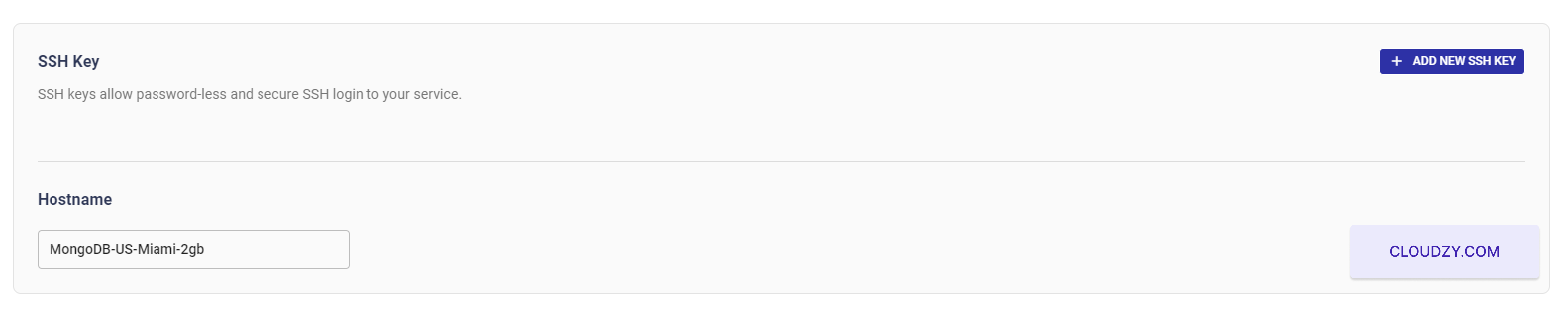
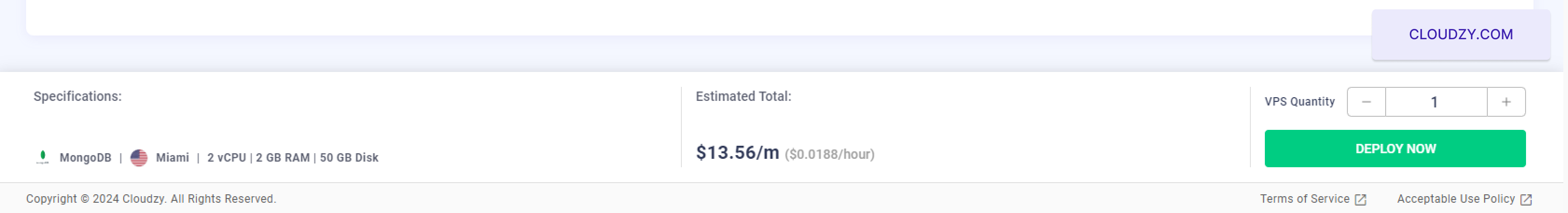 The setup will begin, and your server will
The setup will begin, and your server will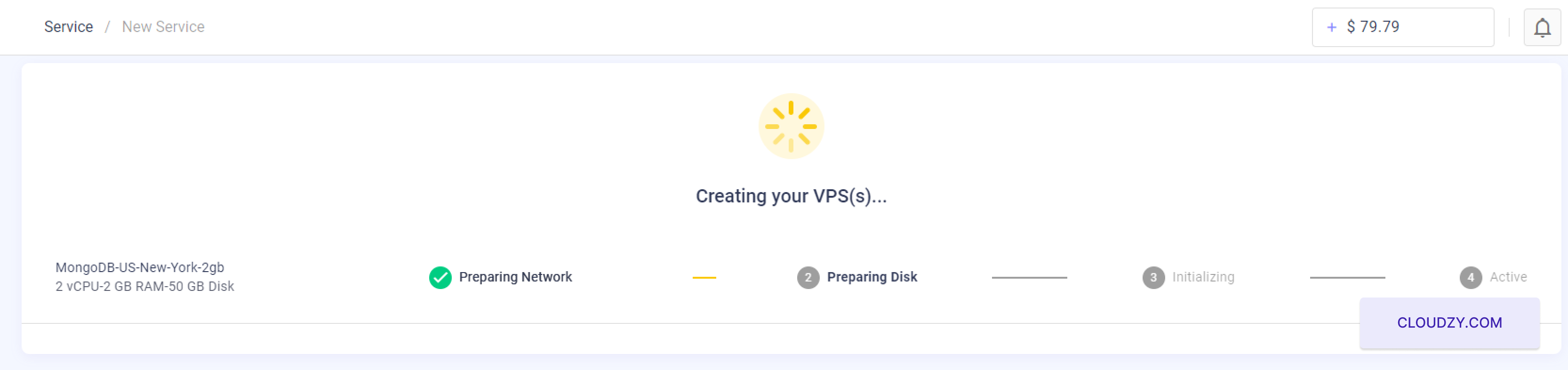
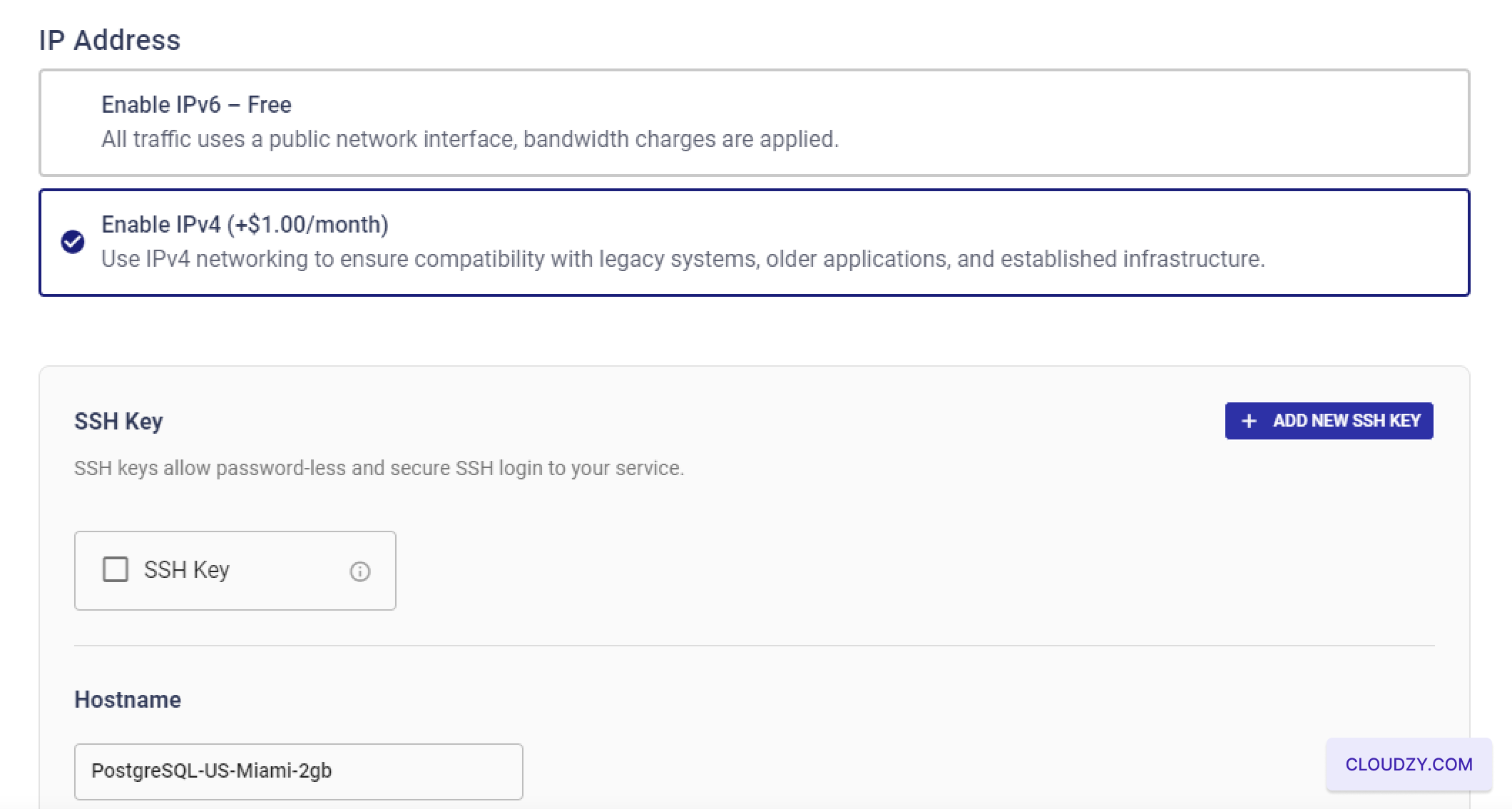
 If you want to use SSH keys for
If you want to use SSH keys for
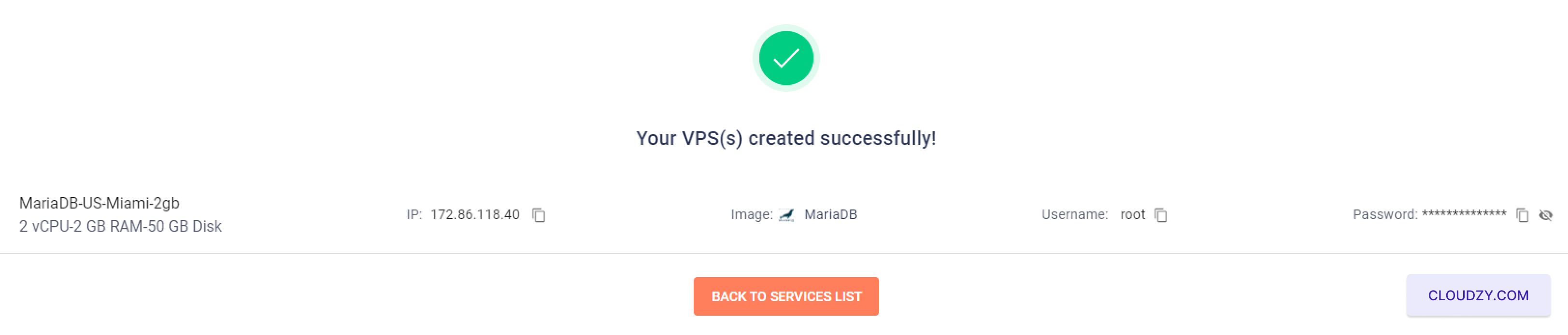


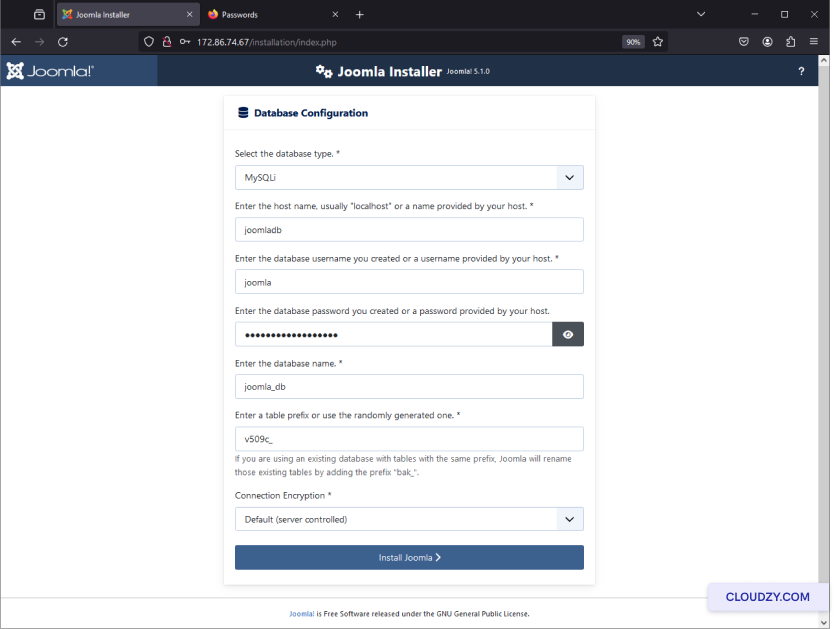
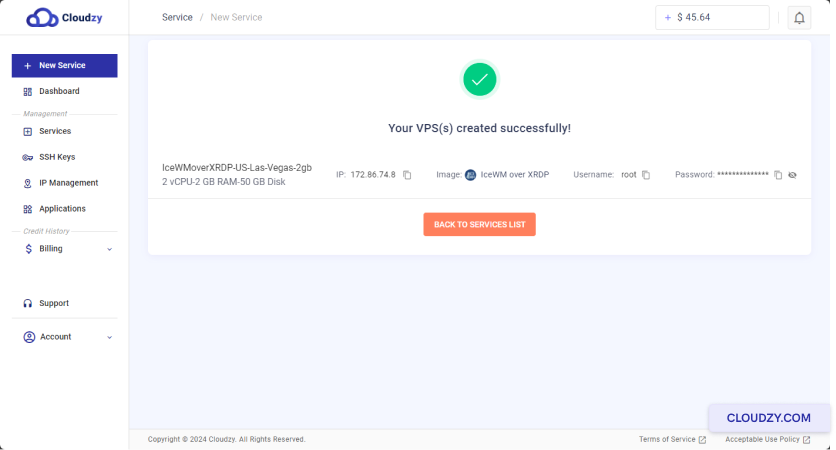
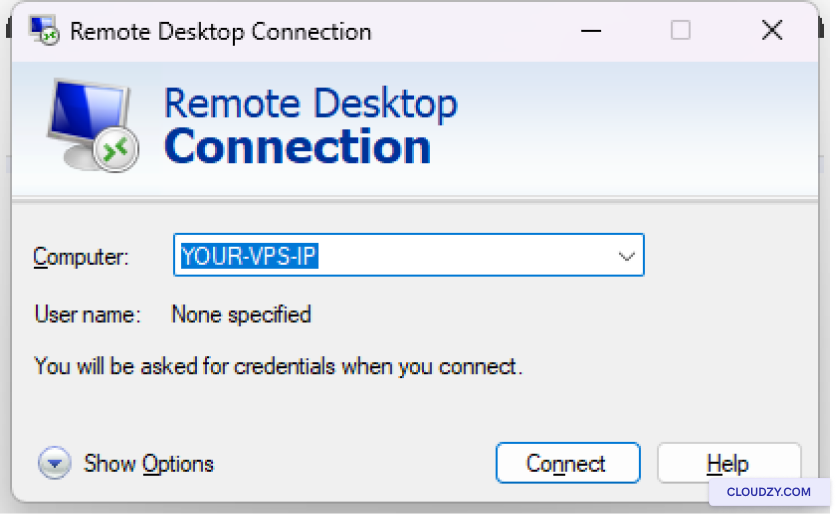
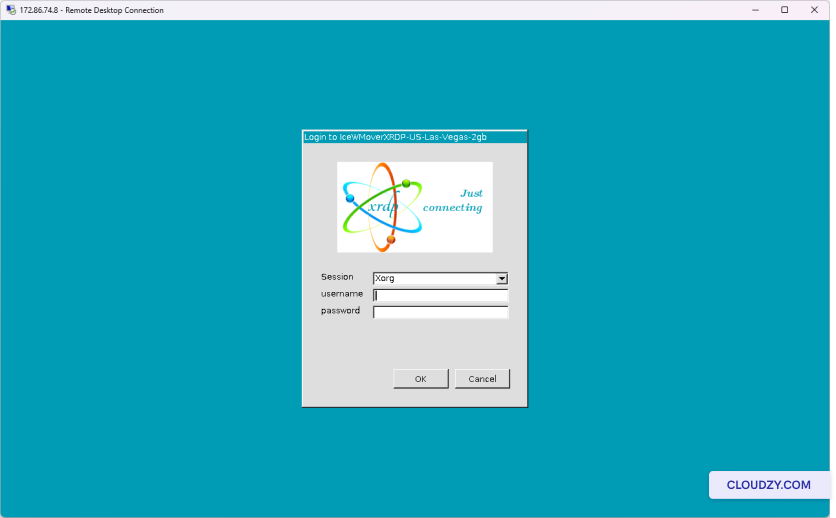

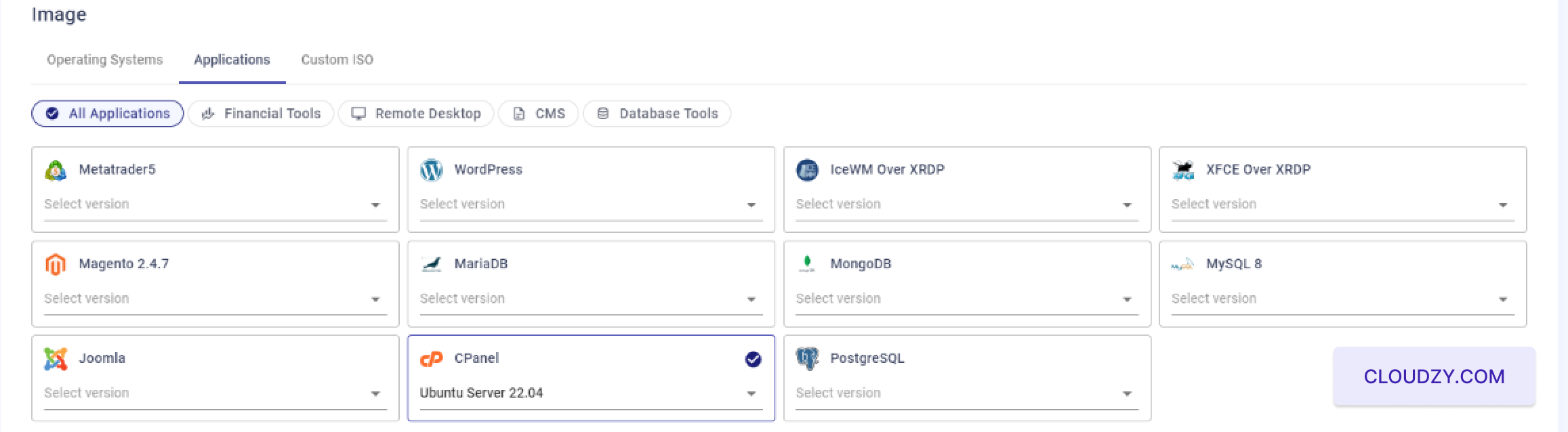
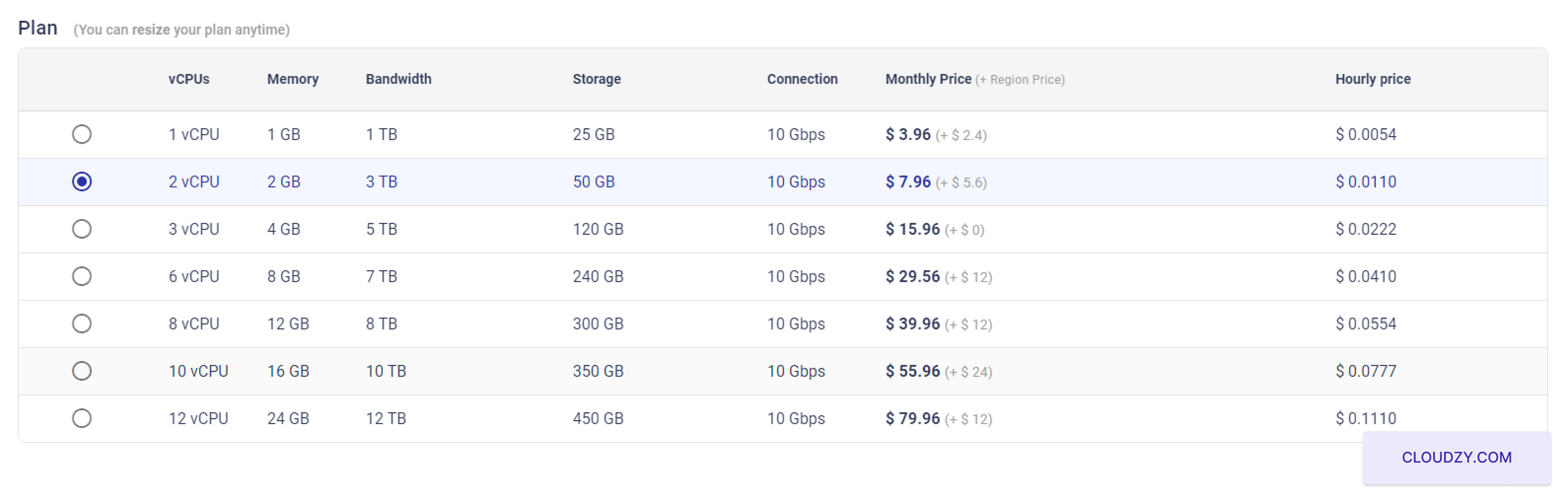
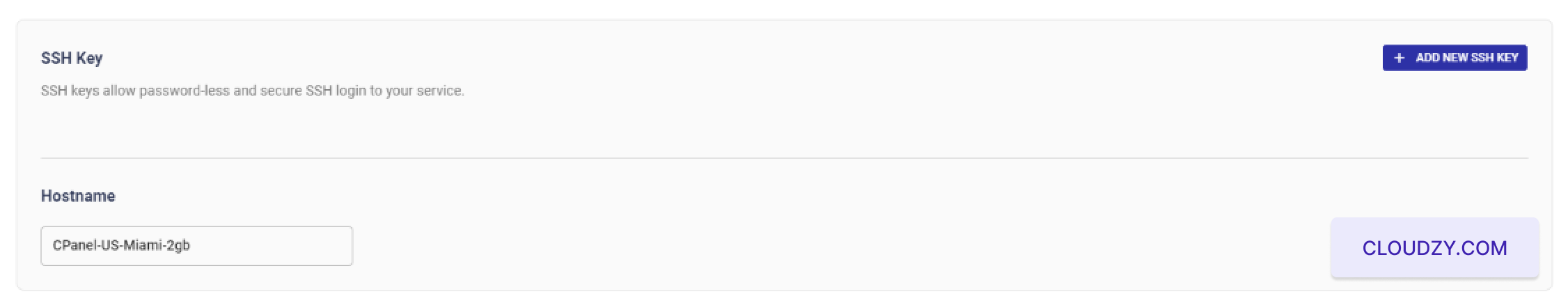
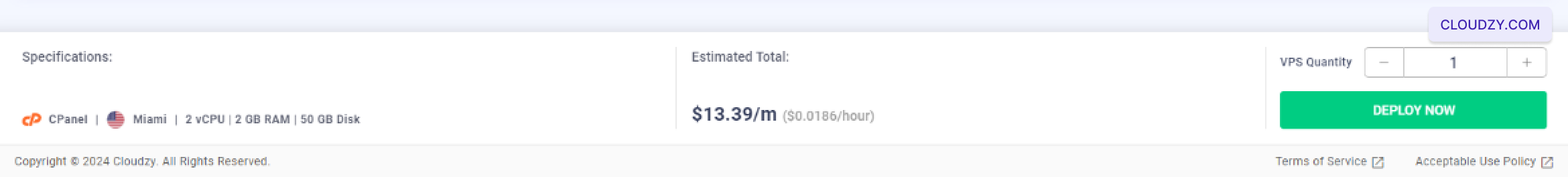

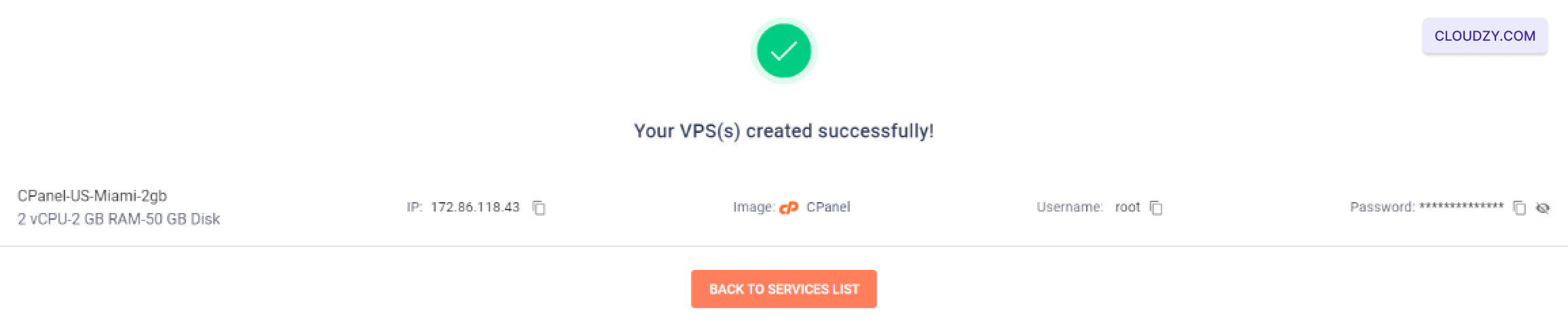

 Following these steps, your cPanel
Following these steps, your cPanel