Troubleshooting connectivity issues on a Cloud Virtual Private Server
(VPS) often involves examining and adjusting the firewall settings. A
properly configured firewall is essential for maintaining optimal
security while ensuring that services remain accessible. This article
provides a comprehensive guide on how to manage and troubleshoot your
VPS’s firewall settings for improved connectivity.
Prerequisites
Before diving into the firewall troubleshooting steps, ensure you
meet the following prerequisites:
-
Sudo Privileges: You should have sudo privileges
on your VPS to execute administrative commands. -
Basic Firewall Knowledge: Familiarity with basic
firewall concepts and commands, specifically for UFW (Uncomplicated
Firewall), used in this guide. -
SSH Access: Ensure you have SSH access to your
VPS for remote command execution. -
Updated System: Your VPS should be running an
up-to-date version of its operating system for security and
compatibility. To update your system, log in to your VPS and run these
two commands:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade.Step 1: Check Firewall
Status
- Check the firewall status:
Begin by checking the current status of your firewall with:
sudo ufw statusThis command will display whether the firewall is active and show any
existing rules.
- Activate Firewall If Inactive:
You’ll need to enable the firewall if it’s not active. Before doing
so, make sure SSH connections are allowed to prevent getting locked
out:
sudo ufw allow ssh
sudo ufw enableThese commands will allow SSH connections through the firewall and
then activate it.
This step is crucial to ensure that your firewall is running and
configured correctly for initial diagnosis.
Step 2: Review
and Modify Firewall Rules
- List Current Firewall Rules:
To view all current firewall rules with their numbers, use:
sudo ufw status numbered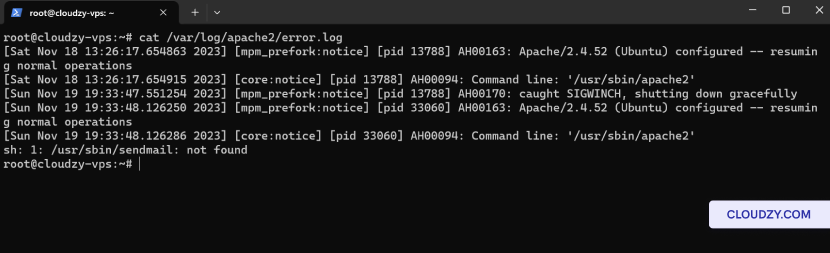
This command provides a clear overview of all the rules and their
sequence.
- Allowing a Specific Port:
To allow traffic on a specific port, execute:
sudo ufw allow [port_number]Replace [port_number] with the actual port number
you wish to open.
- Denying a Specific Port:
To block traffic on a specific port, use:
sudo ufw deny [port_number]Replace [port_number] with the port number you want
to close.
- Deleting a Specific Rule:
To remove a rule, identify its number from the list, then run:
sudo ufw delete [rule_number]Replace [rule_number] with the number corresponding
to the rule you want to delete.
- Recheck Updated Rules:
After making changes, recheck the updated rules with:
sudo ufw statusBy reviewing and modifying the firewall rules as needed, you can
manage the traffic flow to and from your VPS, addressing potential
connectivity issues.
Step 3: Test
Connectivity
- Test Service Connectivity:
-For web services, access your website via a browser. Or you can use
a command like: curl http://your_website.com.
-For SSH, test the connection with ssh
username@your_vps_ip.
-For FTP services, try connecting using an FTP client or command
line: ftp your_vps_ip.
- Verify Access to Allowed Ports:
-
To check if a specific port is accessible, you can use the telnet
command: telnet your_vps_ip port_number. -
For example, to test a web server on port 80: telnet
your_vps_ip 80.
- Check for Blocked Services on Denied Ports:
-
Confirm that connections to denied ports are blocked. Attempt to
connect to a service on a blocked port, and it should fail. -
For instance, if you’ve blocked port 8080, testing with
telnet your_vps_ip 8080 should not succeed.
Including these command examples provides a practical approach to
verifying the effectiveness of your firewall settings.
Step 4:
Additional Troubleshooting Tips
- Verify Service Status:
Make sure the services you’re trying to access, such as web servers
(apache2, nginx) or databases (mysql), are running. Use commands like
sudo systemctl status apache2 to check their
status.
- Check for IP Restrictions:
Make sure no IP-based restrictions are set in the firewall that might
inadvertently block your access. This can be verified with sudo
ufw status.
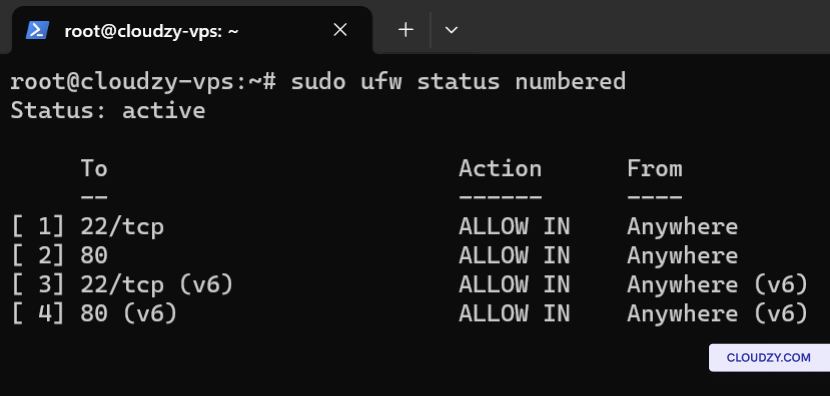
- Review Logs for Clues:
Check server logs for any error messages or clues related to
connectivity issues. For Apache, you might look at
/var/log/apache2/error.log.
- Use Network Diagnostic Tools:
-
Ping: Test network connectivity to your server
(ping your_server_ip). -
Traceroute: Trace the path packets take to your
server (traceroute your_server_ip). This is helpful for identifying
where connectivity issues occur along the route. -
Netstat: Display network connections and
listening ports (netstat -plntu). Useful for seeing what services are
listening on which ports. -
Nmap: Scan for open ports to verify if the
firewall rules are correctly applied (nmap your_server_ip).
These additional steps and tools can help you diagnose and resolve
more complex connectivity issues.
You now know everything about connectivity troubleshooting. If you
have questions or need more information, feel free to contact us by submitting a
ticket!