Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) lets you control a Windows server over the network as if you were using it locally. On Windows Server 2016, RDP is disabled by default because Microsoft recommends using PowerShell and WinRM for remote management and warns that exposing port 3389 without safeguards can invite attacks.
Still, many administrators and remote workers need graphical access to install software, troubleshoot issues, or assist users. This guide explains how to enable RDP in Windows Server 2016 using four different methods while highlighting best practices for security and stability.
Why Enable RDP & Prerequisites

RDP is useful when a graphical interface is necessary ( see what is RDP). However, enabling it should be an intentional choice. Before you proceed with learning how to enable RDP in Windows Server 2016, confirm the server is patched and sits behind a trusted firewall.
Log in with an administrator account, know the machine’s IP address or DNS name, and make sure you can reach it over a secure network or VPN. The Windows Firewall will need to allow incoming traffic on TCP port 3389.
Here are key prerequisites:
- Administrator rights: Only administrators can switch on RDP.
- Network access: Make sure you can reach the server and that port 3389 is open.
- User accounts: Decide which non‑admin users need remote access so you can add them later.
- Security planning: Plan to use Network Level Authentication (NLA), strong passwords, and limit exposure to trusted IP ranges.
Once you meet these requirements, choose a method below and follow the steps on how to enable RDP in Windows Server 2016.
Method 1: Enable RDP via Server Manager (GUI)

If you have no clue about how to enable RDP in Windows Server 2016, the GUI method is the simplest:

- Open Server Manager and select Local Server in the left pane. The main pane lists system properties.
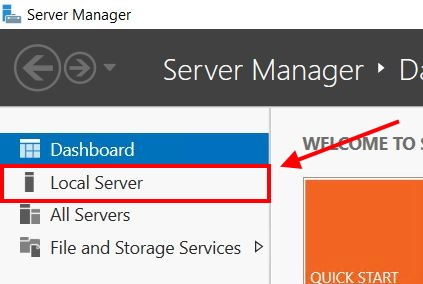
- Change Remote Desktop settings: Next to Remote Desktop, click the blue Disabled link.
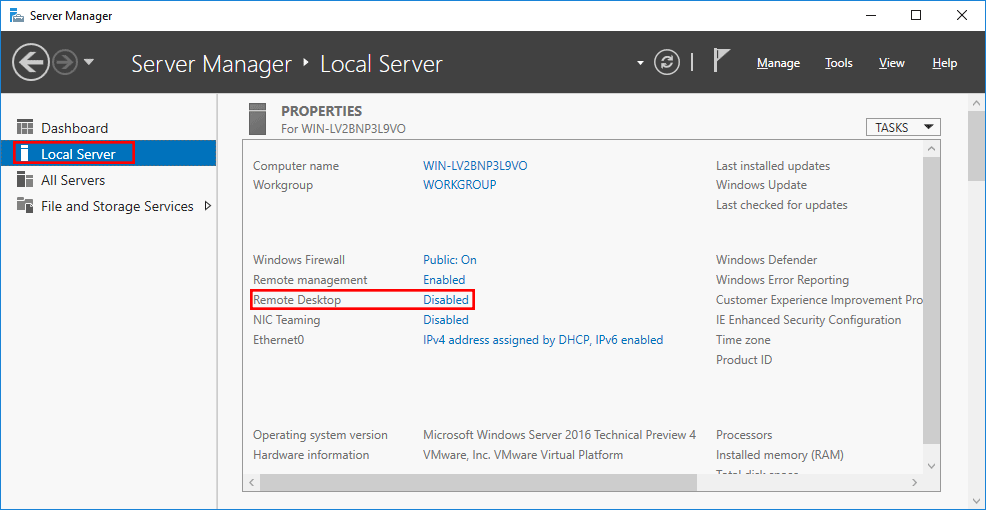
- In the System Properties dialog, select Allow remote connections and, for better security, check Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication.
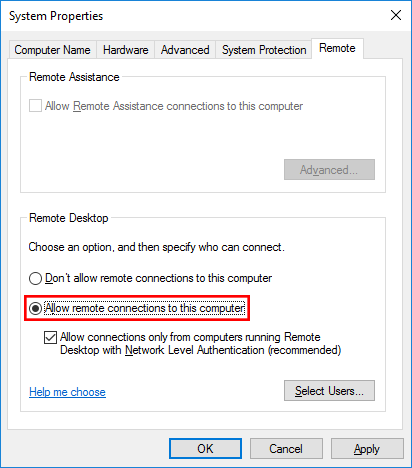
- Apply and add users: Click Apply. A prompt will enable the firewall rule automatically. To allow non‑administrators, click Select Users, add their usernames, and click OK.
- Verify status: Close and reopen Server Manager or press F5. The Remote Desktop entry should show Enabled. Test access from your client machine using the Remote Desktop Connection app.
This method shows how to enable RDP in Windows Server 2016 using the graphical interface; if you prefer scripts, PowerShell is next.
Method 2: Enable RDP Using PowerShell

PowerShell is ideal for automation and remote scenarios. In this section, you will learn how to enable RDP in Windows Server 2016 via the command line:
Enable RDP:
Set‑ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server' -Name 'fDenyTSConnections' -Value 0
Open the firewall rule:
Enable‑NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "Remote Desktop"Optional: enforce NLA and add users:
Set‑ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP‑Tcp' -Name 'UserAuthentication' -Value 1
Add‑LocalGroupMember -Group 'Remote Desktop Users' -Member '<Domain\Username>'
These commands modify the registry value controlling RDP and enable the firewall group for port 3389. To run them on a remote server, first establish a session with Enter‑PSSession over WinRM. If you need a text‑only alternative on how to enable RDP in Windows Server 2016, the next method uses Command Prompt.
Method 3: Enable RDP via Command Prompt

If you prefer Command Prompt or are working on systems without PowerShell, you can achieve the same outcome. This approach shows you how to enable RDP in Windows Server 2016 using built‑in tools:
- Open Command Prompt with admin rights.
- Set the registry value:
reg add "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" /v fDenyTSConnections /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
- Enable the firewall rule:
netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group="remote desktop" new enable=yes
- Grant non‑admins access:
net localgroup "Remote Desktop Users" /add <Domain\Username>
- Check your work:
reg query "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" /v fDenyTSConnections
A value of 0x0 confirms remote access is allowed. Close and reopen Server Manager to refresh its status. If you need to enable RDP on many servers at once, the next section shows how to enable RDP in Windows Server 2016 using Group Policy.
Method 4: Enable RDP via Group Policy

Group Policy is suited for domain environments where you need to enable RDP across many servers. Those looking to learn how to enable RDP in Windows Server 2016 for multiple machines can follow these steps:
- Create or edit a GPO: Open the Group Policy Management Console by searching for it in Start. Right-click your domain or an organizational unit, and create a new GPO.
- Navigate to the RDP setting: Under Computer Configuration → Administrative Templates → Windows Components → Remote Desktop Services → Remote Desktop Session Host → Connections, double‑click Allow users to connect remotely using Remote Desktop Services.
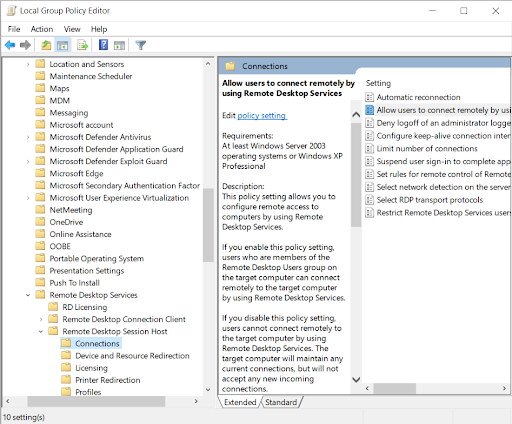
- Enable the policy and optional NLA: Choose Enabled. To enforce NLA, set Require user authentication for remote connections by using Network Level Authentication to Enabled.
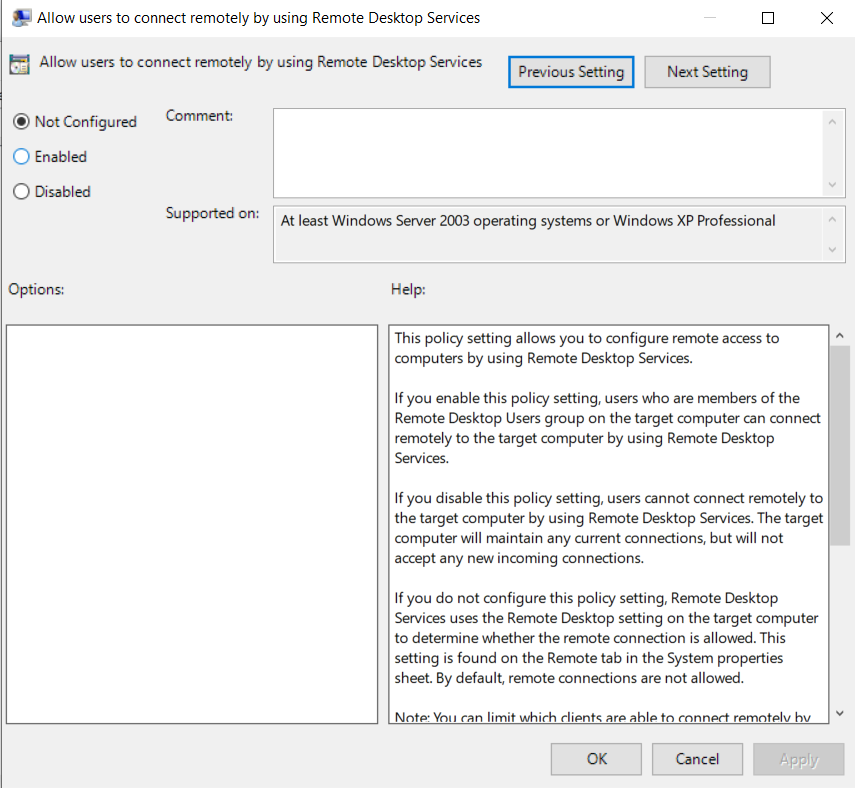
- Update the target servers: Run gpupdate /force on each server or wait for the policy refresh cycle.
This approach standardizes RDP settings and is easier to audit. You can further secure access by editing the firewall rule within the same GPO. If you can’t be bothered with doing all this yourself, you can always go for one of the best RDP providers for commercially managed solutions.
Cloudzy’s RDP VPS
You can even skip searching for the best RDP provider and spin up a Windows virtual desktop with Cloudzy’s RDP VPS. You get full admin access, your preferred Windows Server (2012, 2016, 2019, or 2022) preinstalled, instant activation, and two concurrent logins; the service stays affordable as you grow with PAYG.
Choose one of our many data centers in the USA, Europe, or Asia to keep latency low, then scale CPU, RAM, and storage without migrations. Under the hood, high‑clock CPUs up to 4.2 GHz with DDR5 memory, NVMe SSD storage, and up to 10 Gbps networking keep your desktop responsive, while built‑in DDoS protection, a dedicated static IP, 99.95% uptime, and 24/7 support keep you online. Flexible payments include cards, PayPal, Alipay, and crypto. When you are ready, buy RDP.
Firewall Configuration & Security Best Practices

Turning on RDP exposes your server to remote login attempts. Adopt these best practices to minimize risk after you learn how to enable RDP in Windows Server 2016:
- Restrict inbound traffic: Limit the firewall rule to specific IP ranges. If you don’t need access from the open internet, allow connections only from your VPN or corporate network.
- Use a VPN: Provide remote users with a VPN tunnel so RDP is never exposed directly to the public internet.
- Require NLA and strong passwords: NLA authenticates users before they see the desktop. Combine it with complex passwords and multi‑factor authentication through your identity provider or hardware tokens.
- Change the default port: Changing port 3389 to a non‑standard number via the registry can reduce automated scans. Remember to adjust firewall rules and client settings accordingly.
- Keep systems updated: Apply the latest Windows updates and security patches. Exploits targeting RDP often rely on outdated software.
Balanced against convenience, these measures help keep your server safe. That said, you can always try an RDP alternative like VNC.
Troubleshooting & Remote‑Access Tips

Even when correctly configured, you may run into issues connecting via RDP. If you’ve followed the steps on how to enable RDP in Windows Server 2016 and still can’t connect, here are a few things you can try:
- Firewall blocks: The Windows Firewall rule may still be disabled, or an external firewall might block port 3389. Review your rules and confirm the port is open.
- Permissions errors: Only administrators and members of the Remote Desktop Users group can connect. Add necessary users to that group.
- Network instability: High latency or VPN disruptions can cause timeouts. Use a stable connection and test from another network if possible.
- Status not refreshed: Server Manager may still report RDP as disabled until you refresh it with F5 or reopen the console.
- Client software: Use the official Microsoft Remote Desktop client for your operating system. On macOS, install Microsoft Remote Desktop from the App Store; on Linux, use Remmina. Android and iOS users can find the mobile client in their respective app stores.
If you prefer to avoid managing RDP yourself after learning how to enable RDP in Windows Server 2016, look into a Windows Server 2016 VPS that comes with remote access preconfigured.
Final Thoughts
Enabling remote access is straightforward once you know how to enable RDP in Windows Server 2016. Choose the Server Manager method for simplicity, PowerShell or Command Prompt for scripting and remote scenarios, and Group Policy for domain‑wide consistency.
Regardless of method, secure the server by restricting inbound connections, enabling Network Level Authentication, and granting access only to required users. Don’t forget to test and troubleshoot your setup to make sure you have a reliable connection. Lastly, once again, if you’d rather not worry about configuration, consider a managed RDP VPS from Cloudzy to avoid all that hassle.



