Encountering the Blue Screen of Death is frustrating, but when you see Kernel Security Check Failure flash across your screen, the diagnostic process becomes even more complex. This BSOD error is one of the most common system failures affecting Windows 10 and Windows 11 users.
The Blue Screen Kernel Security Check Failure signals that your operating system’s kernel has detected corruption in critical data structures. When this error appears, your computer has identified a problem serious enough to halt operations immediately.
This guide explores what triggers this issue and provides nine proven solutions to resolve it on both Windows 10 and Windows 11 systems.
What is the Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)?
The Blue Screen of Death is a critical system error that occurs when Windows encounters an unrecoverable problem. When this happens, the system halts all operations and displays a blue screen with an error message, a QR code, and the phrase “Your PC ran into a problem and needs to restart.”
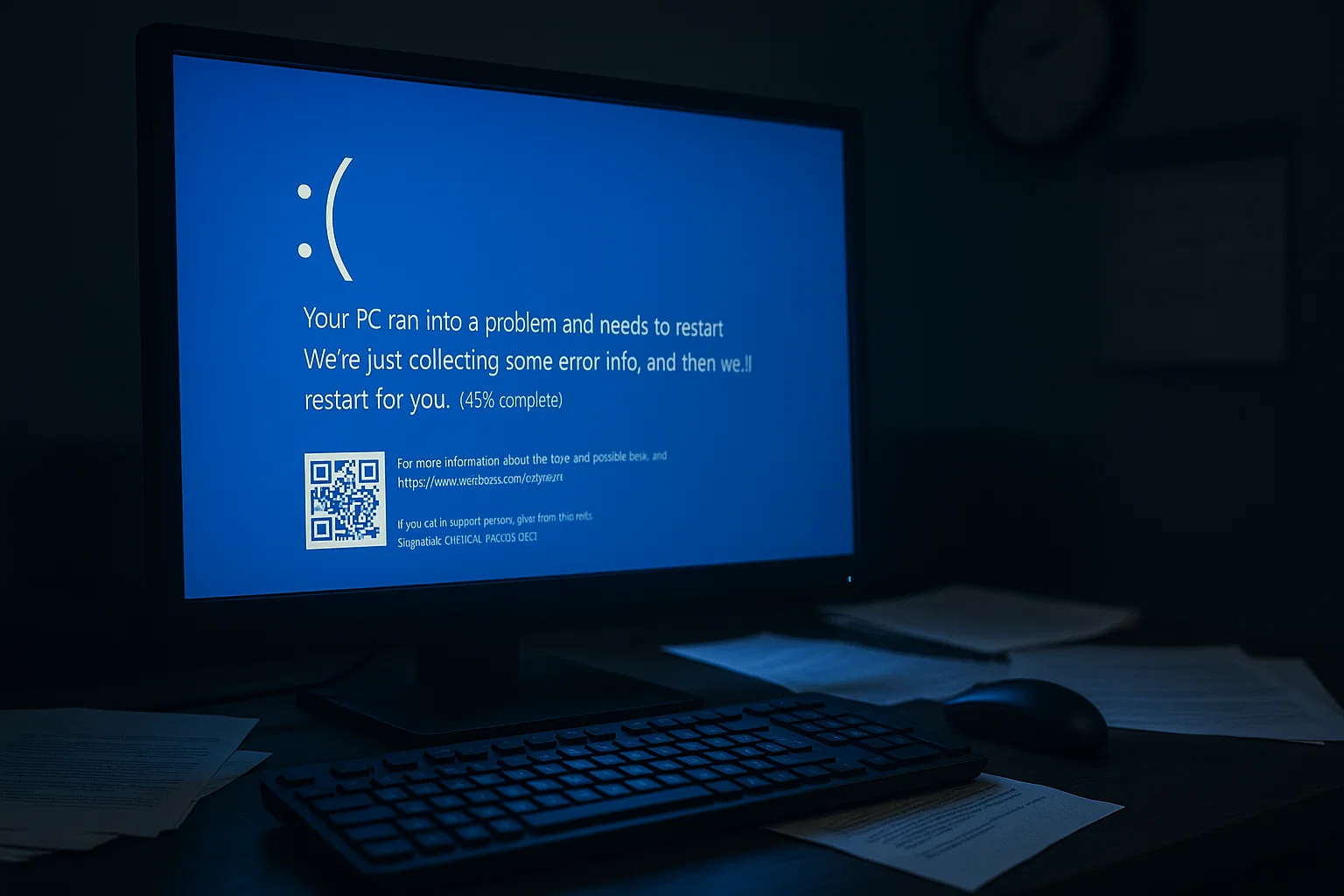
But things look different on Windows 11. The screen is black rather than blue. You also won’t see a QR code. The error text stays the same, so the fixes here still work.
The error message includes specific information about what failed, such as a device driver or hardware component. BSODs stem from various issues, including software bugs, hardware failures, driver conflicts, and malware infections.
One common variant is the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error, which indicates driver or hardware issues causing incorrect memory access.
If your system settings allow it, Windows attempts to create a dump file when a BSOD occurs. This file contains detailed information about the system’s state at the time of the crash. This file serves as a diagnostic snapshot, allowing you to analyze what went wrong and determine the appropriate fix.
BSODs can cause data loss when the system shuts down unexpectedly, so you need to fix them right away. Start with diagnostic tests and check for software conflicts. If those don’t work, you might need a system restore or a clean Windows installation.
The Kernel Security Check Failure Blue Screen is one of these errors that requires immediate attention.
What Causes Kernel Security Check Failure
Before diving into causes, you need to identify this specific error. When the BSOD occurs, check the bottom of the screen for a stop code.
If you see the phrase “kernel_security_check_failure” displayed, you’ve confirmed this exact error. This stop code distinguishes it from other BSOD errors and helps guide your troubleshooting approach.
Multiple factors can trigger this issue on Windows systems. Identifying the root cause helps determine the most effective solution.
Bug Check 0x139
The technical identifier for this error is Bug Check 0x139, also known as KERNEL_SECURITY_CHECK_FAILURE.

This bug check indicates that the kernel has detected corruption in a critical data structure, such as a stack cookie, LIST_ENTRY corruption, or an invalid parameter. This is typically caused by a buggy driver or software overwriting memory it does not own, rather than a malicious attack.
This technical classification helps when analyzing crash dump files, as the parameters often point to the specific driver responsible for the corruption.
Corrupted System Files
System file corruption is one of the main causes of Kernel Security Check Failure errors. Corruption occurs through malware infections, disk errors, improper shutdowns, or failed Windows updates. When core Windows files become damaged, the kernel struggles to execute essential functions, triggering the security check failure.
Outdated or Incompatible Drivers
Drivers connect your operating system to hardware components like graphics cards and network adapters. When drivers become outdated, incompatible with your Windows version, or contain bugs, they can access memory incorrectly or perform unauthorized actions.
The kernel detects this abnormal behavior and shuts down the system to prevent damage. The system displays the KERNEL_SECURITY_CHECK_FAILURE stop code, while the crash dump captures the technical details needed for diagnosis. Many programs help you monitor drivers and keep them updated to prevent this issue.
Faulty Hardware
Faulty hardware components, such as RAM, hard drives, and motherboards, frequently cause Kernel Security Check Failure errors. When these components become damaged or fail, the kernel may be unable to access or manage system resources properly. This represents the worst-case scenario, as you’ll need to either pay for repairs or purchase replacement parts.

Malware Infections
Malware can compromise system security by corrupting files, altering permissions, or interfering with kernel operations. Some malicious software attacks kernel-level processes directly, causing this type of BSOD. Maintaining active antivirus protection with Windows Security or reputable third-party security software helps prevent these attacks.

Overclocking
Overclocking pushes CPU or GPU performance beyond manufacturer specifications to boost speed. However, incorrect settings or poor cooling cause system instability that can trigger kernel security errors.
The increased power consumption and heat generation from overclocking stress components can lead to crashes. If this issue appears after adjusting performance settings, return components to stock speeds.
How to Fix Kernel Security Check Failure
Now it’s time to address the Kernel Security Check Failure issue with proven solutions. The following nine methods work for both Windows 10 and Windows 11 systems. Try them in order, and most users find their problem resolved before reaching the final solution.
Use Safe Mode to Narrow Down Options
Important Warning: Before entering Safe Mode, ensure you have your BitLocker recovery key available. Changing boot settings can sometimes trigger BitLocker recovery mode, and you will need this key to access your system.
The first method to resolve the kernel_security_check_failure is booting in Safe Mode. This diagnostic mode starts Windows with only a minimal set of drivers and services, rather than your full standard environment.
If you boot in Safe Mode and do not encounter the issue, it suggests the problem is likely caused by a third-party driver, recently installed software, or a non-essential service.
To boot in Safe Mode:
- Click the Windows Start button and select Restart while holding the Shift key.
- Your PC will restart to the Choose an option screen.
- Select Troubleshoot, then Advanced options, then Startup Settings, and click Restart.
- After your PC restarts, you’ll see a list of options.
- Press 4 or F4 to start in Safe Mode, or press 5 or F5 for Safe Mode with Networking.
If your system runs normally in Safe Mode, proceed to check your recently installed drivers and applications.

Update Your Windows
Windows updates often resolve system stability issues and BSOD errors. Installing the latest updates can fix known bugs causing this problem.
To update Windows:
For Windows 11:
- Click the Windows Start button and select Settings (gear icon)
- Navigate to Windows Update from the left sidebar
- Click Check for updates
- Install any available updates
- Restart your computer when prompted
After updating, test whether the BSOD still occurs.
For Windows 10:
- Click the Windows Start button and select Settings (gear icon)
- Navigate to Update & Security, then click Windows Update
- Click Check for updates
- Install any available updates
- Restart your computer when prompted
If the problem persists after updating, continue to the next solution.
Update Your Drivers
Outdated or incompatible drivers represent one of the most common causes of this problem. Updating drivers ensures hardware components communicate properly with Windows.
To update drivers manually:
- Type Device Manager in the Windows search bar and open it
- Locate the device category you want to update (Display adapters, Network adapters, etc.)
- Right-click the device and select Update driver
- Choose Search automatically for drivers
- Windows will download and install updates if available
- Restart your system
To check for driver updates via Windows Update:
For Windows 11:
- Go to Settings > Windows Update
- Click Advanced options
- Scroll down and click Optional updates
- Expand Driver updates and install any available driver updates
For Windows 10:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update
- Click View optional updates
- Expand Driver updates and install any available driver updates
For graphics cards, network adapters, and storage controllers, visit the manufacturer’s website directly to download the latest drivers. Alternatively, use reputable third-party driver update software, but only download from trusted sources.
Check Potential Corrupted Windows System Files
Corrupted system files often trigger kernel-level crashes. Windows includes built-in tools to scan and repair these files. We recommend running DISM first, as it repairs the system image that the System File Checker (SFC) relies on.
Step 1:
Run DISM: DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management) fixes the Windows component store to ensure future repairs work correctly.
Type cmd in Windows search.
- Right-click Command Prompt and select Run as administrator.
- Type: DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
- Press Enter and wait for completion (this can take 20–40 minutes).
Step 2:
Run System File Checker (SFC): Once DISM completes, use SFC to repair specific corrupted files using the healthy component store.
- In the same Command Prompt window, type: sfc /scannow
- Press Enter.
- Wait for the scan to finish.
- Restart your computer if repairs were made.
This order prevents errors where SFC fails because the source files it attempts to copy from are also corrupted.
Check Your RAM
Your memory or RAM card’s faulty performance can cause the Kernel Security Check Failure problem. You can check it for issues by running the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool using these steps:
To run Windows Memory Diagnostic:
- Type Windows Memory Diagnostic in the search bar.
- Select the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool.
- Choose Restart now and check for problems.
- Your PC will reboot and begin testing RAM (expect 20–30 minutes or longer).
- After the restart, the notification often disappears quickly. To verify the results, open Event Viewer, navigate to Windows Logs > System, and look for MemoryDiagnostics-Results (Event ID 1101 or 1201).
If the diagnostic tool finds errors, you’ll need to identify and replace the faulty RAM module. Try reseating your RAM sticks or removing them one at a time to isolate the problematic module.
Check Your Hard Drive
Hard drive errors and bad sectors can prevent the kernel from properly accessing system files, triggering the “Kernel Security Check Failure” error. The CHKDSK utility scans and repairs these disk errors.
To run CHKDSK:
- Press Windows key + R to open the Run dialog.
- Type cmd and press Ctrl+Shift+Enter to run as administrator.
- Type chkdsk C: /f and press Enter.
- You will likely be prompted that the drive is in use. Type Y to schedule the scan for the next restart.
- Restart your computer.
The /f parameter fixes file system errors and is usually sufficient. If you suspect physical drive damage, you can use chkdsk C: /r, but be aware that this performs a deep scan for bad sectors. It takes much longer to finish. Use it only if the standard fix fails.
If CHKDSK finds and fixes errors, but the problem persists, consider upgrading to an SSD. Solid-state drives have no moving parts. This helps avoid the mechanical failures found in traditional hard drives.
Check for Viruses
Viruses and malware rank among the main culprits of the Kernel Security Check Failure issue. First, check for them using Windows Security, the built-in antivirus protection in Windows 10 and Windows 11.
To scan with Windows Security:
- Type Windows Security in the search bar and open it
- Select Virus & threat protection
- Click Quick scan for a fast check of common infection areas
- For thorough scanning, click Scan options and select Full scan
- Windows Security will display scan results and guide you through removing any threats found
For additional protection, consider scanning with Malwarebytes or another reputable anti-malware tool.

Disable Third-Party Antiviruses
Third-party antivirus programs sometimes interfere with core system operations, causing conflicts that trigger the “BSOD Security Check Failure” error people search for. Temporarily disabling your antivirus can help determine if it’s causing the issue.
Each antivirus program has different disable procedures. Consult your antivirus software’s documentation for specific instructions. After disabling the antivirus, restart your computer and check if the BSOD persists.
If disabling the antivirus resolves the problem, consider switching to a different security solution or contacting the antivirus vendor for support. Note that this does not apply to Windows Security, which is designed to work seamlessly with Windows and rarely causes these conflicts.
Reinstall Windows
If all other solutions fail, a clean Windows installation may be necessary. This is a last resort solution that fixes all software-related issues, including corrupted system files, driver conflicts, and problematic third-party software.
A clean Windows installation won’t resolve hardware-related problems, but it helps identify whether the issue stems from software or hardware. If the problem persists after reinstalling Windows, you can conclude that faulty hardware is the culprit.
Sometimes you need a stable environment to test solutions without risking your main system. That’s where things get tricky with a single machine that keeps crashing.
At Cloudzy, our Windows VPS gives you an isolated testing ground to diagnose BSOD issues safely. Run system checks, test driver updates, or reinstall Windows without touching your primary setup.
With full admin access and 99.95% uptime, you won’t lose progress mid-troubleshooting. Perfect for IT pros who need reliable environments to nail down what’s actually causing the crashes.
Wrapping Up
The Kernel Security Check Failure issue can stem from various causes, including corrupted system files, outdated drivers, faulty hardware, malware infections, or software conflicts. While this Kernel Security Check Failure BSOD is disruptive and concerning, the nine solutions provided should help you resolve it.
Start with simpler solutions like Safe Mode diagnostics and Windows updates before moving to more complex fixes like hardware testing or reinstalling Windows.
Most users find success with driver updates, system file repairs, or RAM diagnostics. Regular updates, basic maintenance, and not installing random software go a long way toward avoiding this BSOD in the future.
By understanding what causes this problem and following these troubleshooting steps, you can restore system stability and prevent data loss. If issues persist after trying all solutions, the problem likely involves hardware failure requiring professional diagnosis or component replacement.



2 thoughts on “Kernel Security Check Failure: BSOD Guide with 9 Solutions”
Kernal Security Scheck Failure on a Dell Precision M 4800. Almost vintage 😉 Hardware can not upgrade to Win 11. I hope it is corrupted system files, but I may be on Newegg soon. Thanks for the article.
Great website you have here but I was curious if you knew of any forums
that cover the same topics talked about here?
I’d really love to be a part of group where I can get suggestions from other experienced people that share the same
interest. If you have any recommendations, please let me know.
Appreciate it!