Remote access has become a standard in modern work environments. It helps office workers connect to their computers from home while being the perfect excuse for an IT administrator to not work onsite. No matter the use, choosing between different protocols affects everything from your connection speed to your security posture.
When people compare RDP vs VNC, they’re looking at two fundamentally different approaches. RDP creates separate virtual workspaces for each user and sends efficient commands rather than images. This makes it faster in Windows environments. VNC takes the opposite approach by capturing and transmitting actual screen images. While this makes it slower, it also means much better compatibility across different operating systems and hardware configurations.
Both protocols let you control computers as if you were sitting right in front of them. RDP shines when you need to share server resources among multiple users, each working in their own independent workspace. VNC excels at team screen sharing, perfect for tech support scenarios and teaching environments where everyone needs to see the same thing.
This guide walks through performance differences, security considerations, platform support, and real-world use cases. You’ll know which one fits your specific needs.

What Is RDP?
Remote Desktop Protocol is Microsoft’s solution for controlling computers and servers remotely. The way it works differs fundamentally from most remote access technologies, and understanding this matters if you’re choosing between protocols.
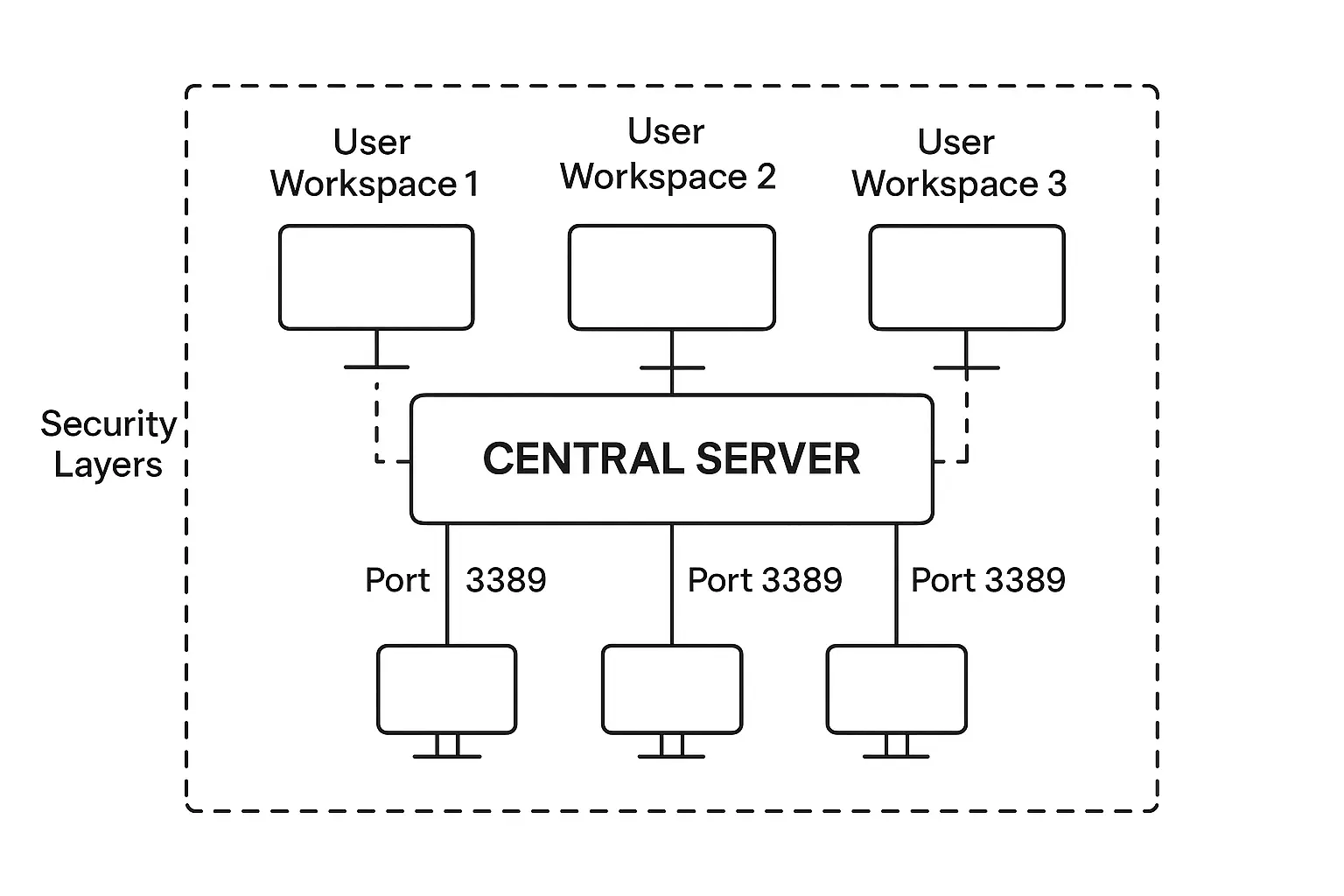
RDP creates a virtual session on the remote computer rather than just showing you what’s on its screen. When you connect through RDP, you get your own separate workspace on that machine, complete with its own login session. This approach follows the T.120 protocol family standards and connects through network port 3389 by default.
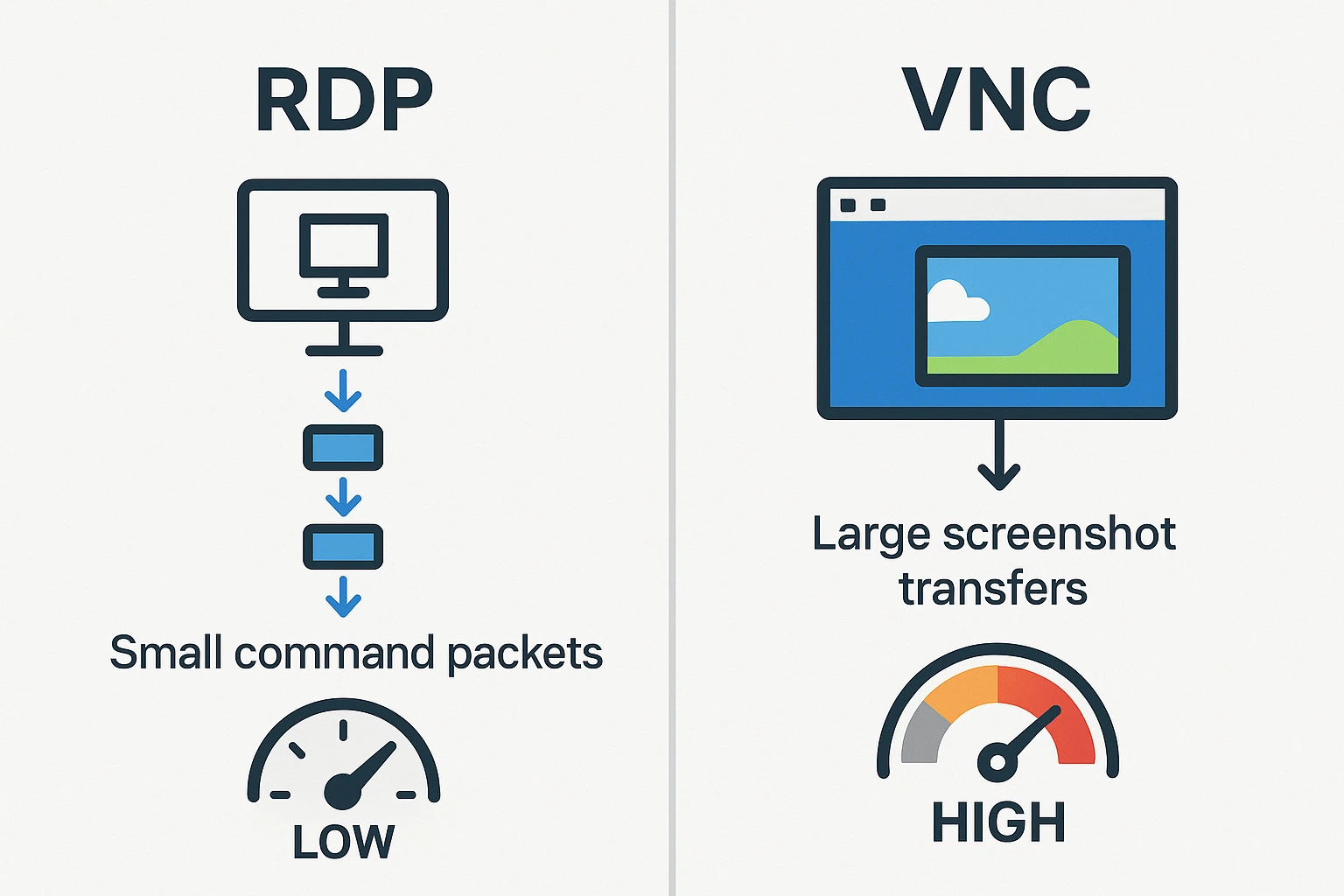
What makes RDP particularly efficient is how it handles data transfer. Instead of capturing and sending images of the screen, it sends instructions about what to display. Your local computer receives commands like “draw a button here” or “display this text” and renders them locally. This requires far less bandwidth than sending actual screenshots. Some RDP clients include additional compression features that speed things up even on slower connections.
Windows includes RDP as a native feature. If you’re running Windows, you already have access to it. Client applications exist for Linux, macOS, iOS, and Android as well. You can connect from pretty much any device. If you want to understand the full capabilities of this technology, our detailed guide on “what is RDP” covers everything from basic setup to advanced configurations.
What Is VNC?
Virtual Network Computing takes a completely different approach to remote access. Instead of creating separate sessions or sending rendering instructions, VNC captures the actual screen content and transmits those images to your device. Think of it like streaming a video of the remote computer’s display in real time.
The protocol uses something called the Remote Framebuffer Protocol (RFB) to handle the communication. Because it’s working with actual pixels rather than abstract commands, VNC can display anything that appears on the remote screen exactly as it looks there. This pixel-based method makes VNC slower than command-based protocols, but it also means VNC doesn’t care what operating system you’re running or what applications you’re using.
I’ve seen VNC save countless hours in tech support scenarios. When you’re helping someone troubleshoot a problem, you both see exactly the same screen. You can guide them through steps while they watch in real time, or you can take control and show them how to do something. Try explaining printer configuration over the phone versus actually showing someone where to click. You’ll understand why support teams prefer VNC.
The platform independence is VNC’s biggest strength. Applications like TightVNC and RealVNC work across Windows, macOS, Linux, and even Raspberry Pi systems without requiring different setups for each. VNC connects through port 5900 by default. While there are dozens of VNC implementations, they all speak the same basic protocol language.

Similarities between RDP and VNC
Before we get into what separates these protocols, understanding their common ground helps clarify where they actually diverge. Both RDP and VNC exist to solve the same fundamental problem: controlling a computer when you’re not physically in front of it.
You need two pieces of software for either protocol to work. The remote machine runs server software that listens for connections. Your local machine runs client software that initiates the connection. Neither protocol routes through third-party services by default. Your computer connects directly to the remote computer, which keeps latency low and reduces potential security vulnerabilities in the connection path.
Both protocols include user management capabilities that let administrators control access. You can specify which users are allowed to connect, monitor active sessions, and set permission levels for different accounts. These features matter in business environments where you need audit trails and access controls.
The similarities end there, though. How each protocol actually accomplishes remote access diverges significantly, and those differences determine which one you should choose for specific situations.
What Are the Differences between RDP and VNC?
Neither protocol wins in every scenario. The difference between VNC and RDP comes down to their fundamental architecture and what they optimize for. This affects everything from performance to use cases.
VNC vs RDP: Functionality & Speed
VNC operates by continuously capturing screen content and transmitting those images across your network. If you’ve ever streamed a video, that’s essentially what VNC does with your remote desktop. Every pixel that changes gets captured and sent to your device, which then displays it. This approach makes VNC slower than alternatives, particularly when you’re working with high-resolution displays or making frequent screen changes.
RDP works at a much lower level. When you click a button or type text on a remote Windows machine, RDP doesn’t capture that action as an image. It sends a command that says “user clicked this button” or “display this text in this window.” Your local computer then renders those actions using its own resources. The amount of data traveling across the network drops dramatically compared to sending full-screen captures.
The session management differs, too. RDP creates actual desktop sessions on the remote computer. If five people connect to the same Windows server through RDP, they each get their own workspace with their own files, settings, and running applications. Nobody sees what anyone else is doing.
When comparing XRDP vs VNC performance, XRDP typically comes out ahead because it brings that same command-based efficiency to Linux systems. XRDP is basically an open-source implementation of RDP that runs on Linux. It focuses on resource sharing rather than screen mirroring. Users generally notice faster response times and smoother performance with XRDP compared to VNC on the same network conditions.
Remote Desktop Protocol Use Cases
VNC functions primarily as a screen-sharing tool where everyone connected sees the same display. All users share one screen, one keyboard, and one mouse. This design makes VNC perfect for specific scenarios that need collaborative viewing.
I’ve watched IT support teams solve problems in minutes using VNC that would have taken hours over the phone. The technician sees exactly what the user sees, can take control to demonstrate solutions, and the user learns by watching. That’s infinitely more effective than trying to guide someone through menu systems they’ve never seen before.
RDP serves a completely different purpose as a resource-sharing platform rather than a screen-sharing one. Each user connects to their own independent session on the remote computer or server. If ten people connect to a Windows server through RDP, they’re all working in parallel. Everyone has access to the server’s processing power, storage, and installed applications, but they’re all working in separate environments that don’t interfere with each other.
With VNC, those same ten users would be fighting over one shared screen. They’d all be moving the same mouse cursor and typing into the same applications simultaneously. You can imagine the chaos.
VNC Performance vs RDP Performance
RDP connects you to Windows computers virtually, regardless of your physical location. The protocol delivers fast response times because it’s only sending display commands rather than full-screen images. This efficiency explains why RDP is the standard choice for accessing virtual private servers where multiple users need to tap into the same physical hardware simultaneously.
VNC’s shared desktop approach introduces performance challenges that become more noticeable as you add users. With one person connected, VNC works reasonably well. Add a second person, and you start noticing slight delays. Add three or four people, and the latency becomes problematic because the system is constantly capturing, compressing, and transmitting screen updates to multiple clients.
The bandwidth requirements tell the story. VNC needs to send continuous screen captures, which uses significantly more network bandwidth than RDP’s instruction-based approach. On slower internet connections, this difference becomes really apparent. RDP sessions remain responsive even on modest connections. VNC sessions start to feel sluggish.
Supported Platforms
RDP comes pre-installed on every Windows computer as a native feature. If you’re running any version of Windows, you already have the RDP server component built in and ready to accept connections. Microsoft also provides RDP client applications for Linux, macOS, iOS, and Android. You can connect to Windows machines from pretty much any modern device.
The RDP vs VNC Linux situation gets interesting because Linux doesn’t include native RDP server support. XRDP fills this gap as an open-source implementation that allows Linux servers to accept connections from Windows RDP clients. When you’re comparing XRDP vs VNC on Linux, the decision often comes down to whether you prioritize Windows compatibility or prefer VNC’s simpler setup process.
VNC achieves true platform independence. The same VNC software works identically across Windows, macOS, Linux, and specialty systems like Raspberry Pi. There are no platform-specific versions or compatibility concerns. If you’re running a mixed environment with different operating systems, VNC eliminates the complexity of managing different remote access tools for different machines.
For Raspberry Pi XRDP vs. VNC specifically, XRDP delivers better performance when your clients are Windows machines, but VNC offers broader client support and an easier initial configuration. Many Raspberry Pi projects use VNC because it’s already included in the default Raspbian installation.
RDP vs VNC: Security Issues
Understanding RDP vs VNC security differences matters because you’re potentially exposing your systems to remote access. Remote Desktop vs VNC security implementations vary significantly in their default configurations and available protections.
RDP operates within an encrypted channel by default on modern Windows versions. The protocol scrambles your data during transmission, so intercepting the network traffic doesn’t expose your keystrokes or screen content. Microsoft has improved RDP’s encryption with each Windows release. Current versions support SSL/TLS encryption on Windows Vista and later, including Windows 7, 8, 10, 11, and all Windows Server versions from 2003 onwards.
Older RDP versions did have vulnerabilities to man-in-the-middle attacks where attackers could potentially intercept sessions. Microsoft patched these issues years ago, but if you’re running ancient Windows versions, that’s something to be aware of. Modern RDP with Network Level Authentication enabled requires users to prove their identity before the connection even establishes. This blocks the most common attack vectors.
When people ask, “Is VNC more secure than RDP?” the answer is usually no. VNC’s default security is weaker than RDP’s because encryption isn’t universal across VNC implementations. Some VNC software includes built-in encryption, but many implementations require you to set up SSH tunneling or VPN connections to get equivalent protection. The VNC server security risk increases significantly if you’re relying on basic VNC without additional security layers.
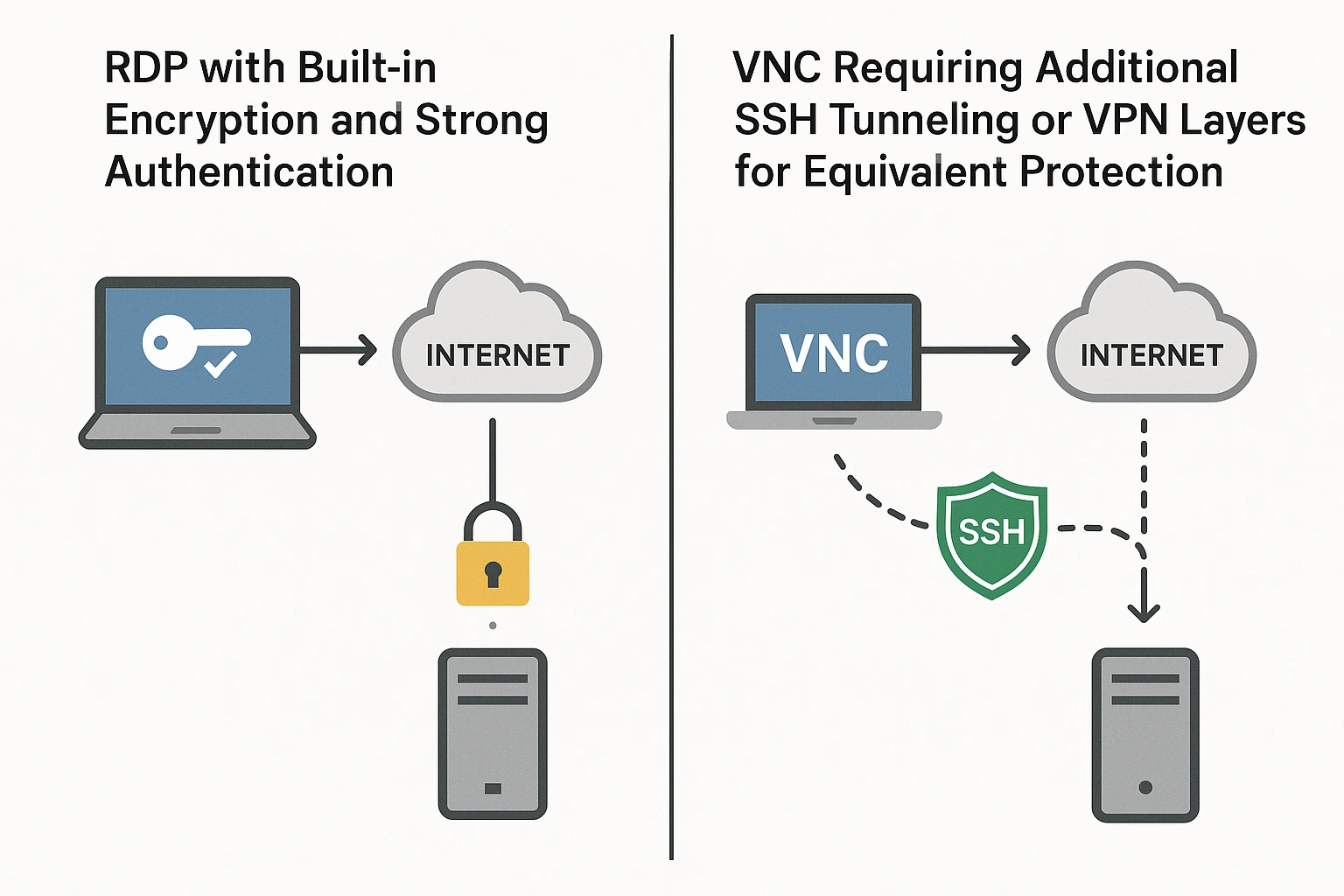
depends entirely on your configuration. VNC can use SSH tunnels to create encrypted protective channels, but this isn’t standard across all VNC software. VNC also grants full remote access by default. This becomes a problem when connecting to computers with sensitive information or administrator accounts that have elevated privileges. To answer the question: “Is VNC Viewer secure?”, it depends entirely on your configuration
Using VNC software without strong password protection greatly increases your risk exposure. I’ve seen systems get compromised simply because someone deployed VNC with a weak password and exposed port 5900 to the internet. RDP generally provides better security out of the box, though both protocols can be configured securely when you take the proper steps.
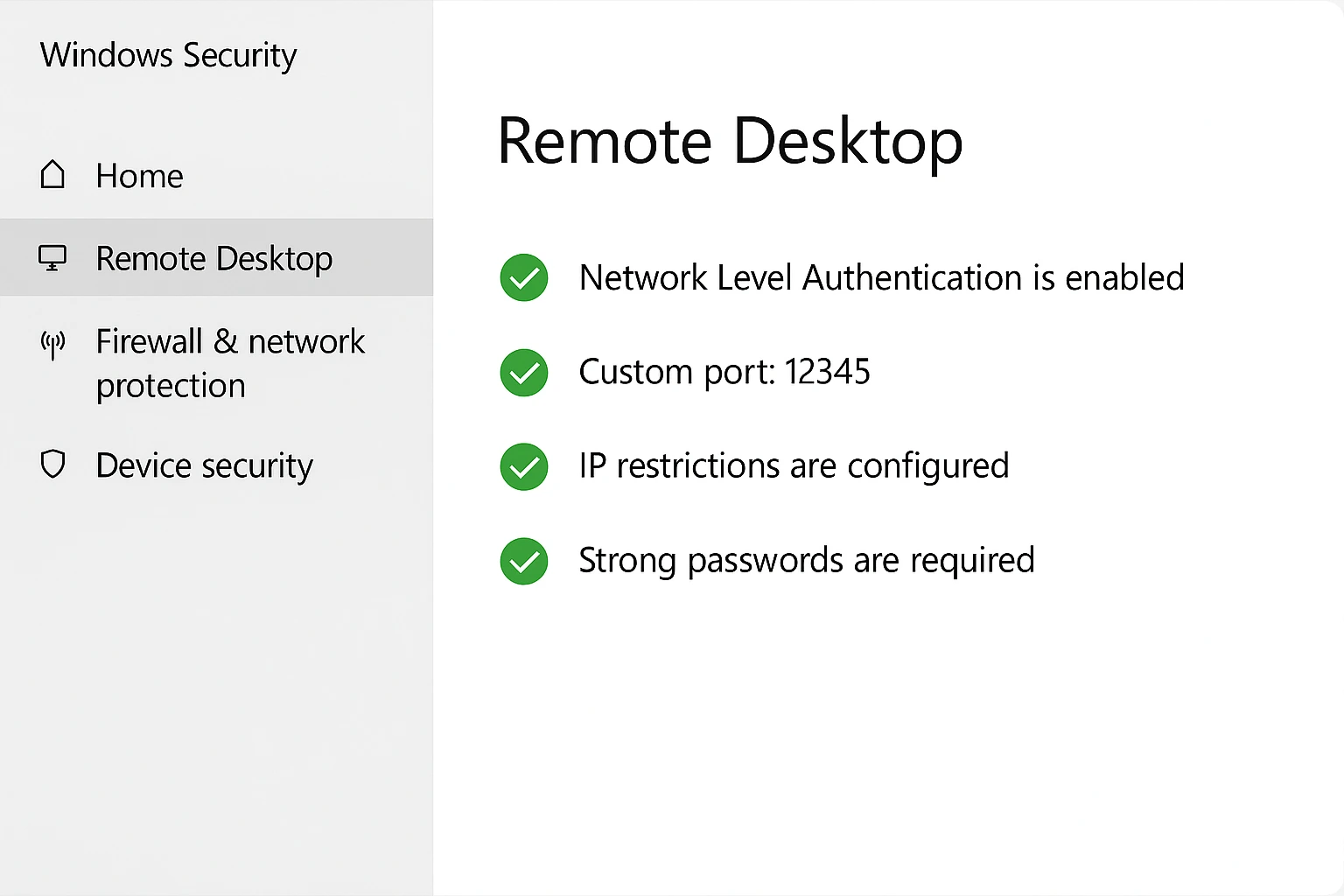
How to Secure RDP
Setting up proper security measures protects RDP connections from the most common attack vectors that target remote access systems.
Enable Network Level Authentication (NLA) first. This setting forces users to authenticate before they even establish a full RDP connection. It works like checking ID at the door before letting someone inside your building, rather than checking after they’ve already entered the lobby.
Configure SSL/TLS encryption on your RDP servers. Modern Windows versions support TLS 1.2 and higher. This provides strong data protection for your remote sessions. The encryption happens automatically on current Windows versions, but verify it’s actually enabled rather than assuming.
Change the default port from 3389 to something else. Automated scanners constantly probe port 3389, looking for RDP servers to attack. Using a non-standard port doesn’t make you invulnerable, but it stops the automated bots that account for most attack attempts.
Set up firewall rules that restrict RDP access to specific IP addresses. If your users always connect from known locations, configure your firewall to only accept RDP connections from those addresses. This dramatically reduces your attack surface because attackers from random IP addresses can’t even reach your RDP service.
Require strong passwords combined with multi-factor authentication. Complex passwords alone aren’t enough anymore. Adding a second authentication factor, like phone-based codes or hardware tokens, creates a crucial additional security layer that blocks most credential-based attacks.
For complete protection strategies beyond these basics, our guide on how to prevent RDP brute force attacks covers advanced security techniques in detail.
How to Secure VNC
Making VNC more secure requires additional configuration because the default settings don’t provide adequate protection for most use cases.
Enable SSH tunneling to wrap VNC traffic in encrypted protection. SSH creates a secure channel that encrypts all VNC communication. This prevents anyone from intercepting your network traffic from seeing your screen content or keystrokes. You’ll need to set up SSH on both the server and client sides before you can tunnel VNC through it.
Use VPN connections for an alternative approach. VPNs create encrypted tunnels for all network traffic between your devices, which includes VNC connections. This adds authentication and encryption layers that protect your VNC sessions without requiring per-application configuration.
Enable built-in encryption in your VNC software if it’s available. Modern VNC implementations like RealVNC offer encryption features that you need to explicitly turn on. Always enable these features rather than relying on unencrypted VNC connections.
To answer “How to make VNC more secure?” I should refer to setting strong passwords that use adequate length and complexity. Avoid default passwords completely. VNC passwords need regular updates. They should be different from your system passwords to limit the damage if one gets compromised.
Restrict server access through firewall rules. Configure your firewall to limit which devices can connect to your VNC server. Allow only specific users and IP addresses rather than leaving VNC accessible to the entire internet.
If your security requirements exceed what VNC can provide, even with these measures, consider a secure alternative to VNC. Professional remote access solutions offer enterprise-grade security features designed specifically for high-risk environments.
When Should I Use RDP, and When Should I Use VNC?
Now that you understand how these protocols work and differ, the decision comes down to matching capabilities to your specific requirements.
When to Choose RDP
Choose RDP when you need to share server resources among multiple users who each need their own independent workspace. The separate session model means everyone can work simultaneously without interfering with each other.
Use RDP for remote access scenarios where you don’t need screen sharing capabilities. If you’re just accessing your own computer remotely to run applications and work with files, RDP’s faster performance makes it the better choice.
RDP handles multi-monitor setups better than VNC. If you’re working with multiple displays on either the local or remote side, RDP’s rendering approach adapts more naturally to complex display configurations.
Windows-focused environments benefit most from RDP because it’s the native remote access protocol for Windows systems. Companies running primarily Windows infrastructure get the best performance and compatibility with RDP.
When to Choose VNC
Choose VNC for team tech support scenarios where both the technician and the user need to see the same screen simultaneously. The shared display model makes collaborative troubleshooting and training much more effective than trying to coordinate through voice alone.
Use VNC for teaching and demonstration purposes when you need to show software procedures to students or team members. Everyone sees the same content in real time. This makes it much easier to teach complex processes step by step.
VNC works better for non-Windows servers running Linux, macOS, Unix, or Raspberry Pi systems. While XRDP exists for Linux, VNC’s universal compatibility often makes it the simpler choice for mixed environments.
Quick Comparison

This RDP vs VNC comparison table summarizes the key differences between these protocols:
| Feature | RDP | VNC |
| Protocol Foundation | T.120 standards | RFB (Remote Framebuffer) |
| Multiple Independent Users | Yes | No (shared screen) |
| Works Across Different OS | Limited (mainly Windows) | Excellent (all platforms) |
| Speed | Fast | Slower |
| Primary Purpose | Resource/data sharing | Screen sharing |
| Supported Operating Systems | Windows, macOS, Linux, Unix, Android, iOS | Windows, macOS, Linux, Raspberry Pi, Android, iOS |
| Connection Port | 3389 (TCP/UDP) | 5900 (TCP) |
| Security Features | SSL/TLS, NLA built-in | Varies (needs setup) |
| Session Type | Independent per user | Single shared session |
| Best Suited For | Windows business setups | Tech support, teaching, mixed platforms |
What Are Some RDP and VNC Alternatives?
Several other remote access solutions exist that might fit your needs better than either VNC or RDP, depending on your specific requirements.
TeamViewer
TeamViewer’s free version provides fast, reliable connections to remote devices with built-in file editing and 3D meeting hosting capabilities.TeamViewer has partnerships with over 100 leading Android device manufacturers, which ensures broad device compatibility.
NoMachine
NoMachine offers completely free remote access with no advertisements or usage restrictions. The software uses NX technology for connection establishment and works across all popular operating systems. NoMachine excels at remote file transfers and provides live audio and video streaming along with session recording for training or documentation purposes.
AnyDesk
AnyDesk provides cross-platform remote computer access and competes directly with TeamViewer. The application supports screen sharing, instant messaging, real-time file sharing, monitoring, and system maintenance. AnyDesk uses RSA 2048 asymmetric encryption for security and functions as a secure alternative to VNC for users who want modern remote access features with strong built-in protection.
For Windows users who need command-line remote access options, our guide on Remote Desktop via CMD explores alternative approaches to remote system management.
Buy VPS Server with Maximum Performance & Zero Security Risks
RDP ranks among the safest remote access protocols when properly configured, but security risks still exist whenever you expose systems to remote connections. Hackers constantly probe for vulnerable RDP servers. Exploiting system weaknesses remains a persistent threat. Using RDP in a properly secured and professionally managed environment protects against DDoS attacks and online threats that target remote access systems.
Cloudzy delivers exceptional RDP performance with zero lag and dedicated, powerful resources. NVMe SSD storage provides the fastest available storage technology for your remote sessions. DDR5 RAM ensures outstanding performance, so all remote desktop operations run smoothly without the slow file transfers or sluggish application response times that plague lower-quality hosting.
RDP comes pre-activated on your VPS with support for two simultaneous user connections. This allows team collaboration where colleagues can work together while maintaining separate, secure sessions for privacy and organization.
Our infrastructure includes robust DDoS protection with continuous monitoring against emerging threats. Multiple server locations exist across the US, Europe, and Asia to ensure low latency regardless of where your users connect from. Your connections stay fast and responsive.
Expert support teams stand ready to help you buy VPS server plans that match your specific needs, whether you need resources for small teams or enterprise-scale deployments. Our experts guide you toward optimal configurations considering your workload requirements and budget constraints.
Experience reliable, fast remote connections with minimal latency while accessing powerful computing resources at competitive prices. Your remote desktop system deserves the performance, security, and reliability that only enterprise-grade VPS hosting provides.
VNC vs RDP Comparison in 2025
RDP delivers superior performance and security for Windows-focused environments, where multiple users can access server resources simultaneously without interfering with each other. VNC provides unmatched compatibility across Windows, macOS, Linux, and Raspberry Pi systems, making it perfect for tech support and educational demonstrations where teams need real-time shared screen access.
Your choice depends on your infrastructure. Windows-focused businesses benefit from RDP’s speed and efficiency. Mixed-platform environments with support or training needs favor VNC’s flexibility and universal compatibility.
Your choice ultimately depends on your remote access requirements and existing infrastructure. Windows-focused companies benefit most from RDP’s speed, efficiency, and native integration. Mixed platform environments with support or training requirements favor VNC, where the protocol’s flexibility and universal compatibility matter more than raw performance.



25 thoughts on “RDP vs VNC : Which Remote Desktop Protocol to Choose?”
VNC and RDP are both useful. I have used both of them in different situations and they are great
Thanks Router👌👌
I love your comparison articles, I read them all 💯
Is it possible to access a computer using a webpage? I mean is there website that can do that? Or it is just possible using a software
If you’re not careful, webpages can access your webcam, microphone and take all kinds of permissions on your computer. Actually, webpages now ask for almost as many permissions as the apps on your phone do. But be careful not to grant these permission if you do not trust the source.
Thank you so much for taking your precious time to read our blog 🌻
What is the best and most powerful client for VNC? Since I am a student I want to know which client of VNC are people using these days
I use anydesk for stablishing connection between android and windows. Which protocol is anydesk using to do so?
AnyDesk uses TLS 1.2, a protocol that is also used in online banking. In addition to that, it works with a 2048bit RSA or 256bit Elliptic curve DH asymmetric key exchange and AEAD to verify every connection.
Thank you so much for taking your time to read our blog 🌻
thanks for this valuable news.
I really need to use VNC for something urgent. I didn’t quite understand how can I use vnc protocol for my needs
What is the difference between a VPS and RDP and VNC?? Because I think VPS actually almost des what RDP and VNC do. By the way great article, thanks!
Does router hosting offer RDP itself?
Where can I find your RDP services and plans!
I believe comparing VNC with RDP is a bit misleading. VNC is a kind of sharing screen platform. To give you a better picture… Using VNC you can help a customer as a part of a CRM system. Whilst, RDP is for a user to have control over another PC in another region. So as to say it works as a VPS.
Any how, thanks for the great work!
In the section about security issues, you are somehow saying that RDP is safer than VNC! or VNC is more secure? could you please clarify. I want to get one and I am not sure if it should be an RDP or VNC!! thanks
Nothing is secure if you put your password as abc123.. u know what i mean…
RDP is considered more secure than remote administration tools such as VNC that do not encrypt the entire session.
Thank you so much for taking your time to read our blog 🌻
I want to get an RDP server for my IOS. Can you please add the guide for IOS configuration of the RDP as well?
Thank you very much for your comment Hakan 😊
I passed your request to our editorial team. They will add the instructions for IOS to the post as well as soon as possible.
My VNC-Server freezes from time to time. Is there a solution to make this stop?
Perhaps a script that can be ran and check if the server still responds. Can you provide that in this article?
Our post with the topic of “RDP vs VNC” is not the best place for this question I think to be answered. However, I will send this to our technical users to add it to our knowledgebase. 😊
Can you mention the difference between RDP vs RDSP? I see somewhere it is called “Remote Desktop” and in some article it is called “Remote Display”. Does it ring any bells?!
RDP or Remote Desktop Connection is a part of the Remote Display Connection or RDSP. This technology was first developed to make it possible for two computers to connect through an internet connection. Hope that helps! 😊
Thank you for introducing AnyDesk. I do have RDP and I like it, but AnyDesk has made screen sharing for me easier than ever. Thank you for the great solution guys. By the way, do you offer RDP as well?
Appreciate your comment! Sure we do offer RDP servers on our own website. 😊
After checking out a handful of the blog articles on your site, I seriously
like your way of writing a blog. I book-marked it to
my bookmark webpage list and will be checking back in the near future.
Please check out my website too and let me know how you feel.