Secure Shell (SSH) is an important protocol for accessing remote
servers in a secure way. Despite its reliability, users may face
connectivity issues when working with SSH. This guide will talk about
typical SSH connectivity problems and provide solutions for diagnosing
and solving them.
Prerequisites
-
Administrative Access: Login credentials with
the necessary privileges on the server you’re attempting to
access. -
Network Access: A stable internet connection and
the ability to reach the server’s network. -
SSH Client: A working SSH client installed on
your local machine, such as OpenSSH or PuTTY. -
Server Information: The server’s IP address, SSH
port number (default is 22), and the appropriate user account
information. -
Permissions: If using key-based authentication,
make sure your private key is available and has the correct permissions
set.
Common Issues and
Causes
Authentication
Failures
These issues arise when there’s a mismatch between the credentials
provided and those expected by the server. Common scenarios include:
-
Incorrect Passwords: Typing errors or recent
password changes can cause failures. -
Public Key Problems: If the server-side
authorized_key file doesn’t contain the correct public
key, or if the client’s private key isn’t loaded, authentication will
fail. -
Expired Credentials: Some systems enforce
password or key expiration policies for security.
Network Problems
Connectivity can be lost by network-layer issues, such as:
-
Firewall Restrictions: Firewalls may be
configured to block the default SSH port (22), requiring a rule change
to allow traffic. -
DNS Misconfiguration: Incorrect DNS settings can
lead to the client resolving to the wrong IP address for the
server. -
Service Interruption: Unreliable internet
connections or server-side networking issues can disrupt SSH
access.
SSH Configuration
Errors
Proper configuration of the SSH daemon and client is essential.
Issues might include:
-
Misconfigured sshd_config: Incorrect directives
in the server’s SSH configuration file can prevent connections. -
Client Configuration Issues: The SSH client
configuration needs to match the server’s requirements, such as
accepting the correct key types or encryption algorithms.
Server Overload or
Downtime
High server load can slow down or disrupt SSH services, and scheduled
or unscheduled downtime can temporarily make the server
inaccessible.
Diagnostic Steps
To identify and address SSH connectivity issues, follow these
diagnostic steps:
Checking Network
Connectivity
Start by confirming that your network connection is active and
stable. Use tools like ping or
traceroute to verify the connection to the SSH server’s
IP address. This will help you determine if the issue is at the network
level.
Verifying
Credentials
Make sure that the SSH credentials you are using are correct and
current. For password-based logins, double-check the password you’re
entering. For SSH key-based logins, confirm that the private key is
loaded in your SSH client and that the corresponding public key is
present in the authorized_keys file on the server.
Inspecting SSH
Configuration
Examine the SSH configuration files carefully. On the server, the
sshd_config file should be configured to permit access
via the intended methods (password or key) and have the correct port
specified. On the client side, the configuration should match the
server’s protocol requirements.
Reviewing Server
Logs
Server logs can provide valuable insights into the cause of SSH
failures. Look for authentication errors or messages related to refused
connections. These logs are typically located in
/var/log/auth.log or
/var/log/secure.
By systematically following these steps, you can narrow down the
cause of SSH connectivity issues.
Troubleshooting
and Solutions for SSH Connectivity
Resolving Network
Issues
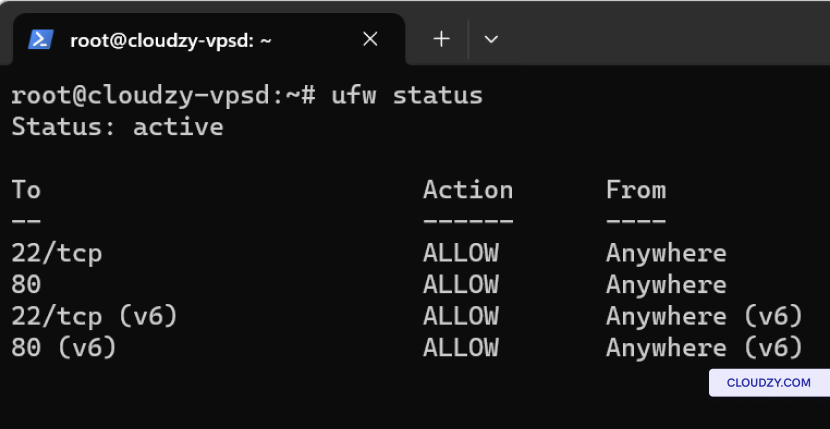
To adjust firewall settings, use the following commands:
-
For Ubuntu: sudo ufw allow 22 to allow SSH
traffic on port 22. -
For CentOS: sudo firewall-cmd –permanent
–add-service=ssh followed by sudo firewall-cmd
–reload.
Fixing Authentication
Problems
If you’re experiencing issues with SSH access due to authentication,
take the following steps:
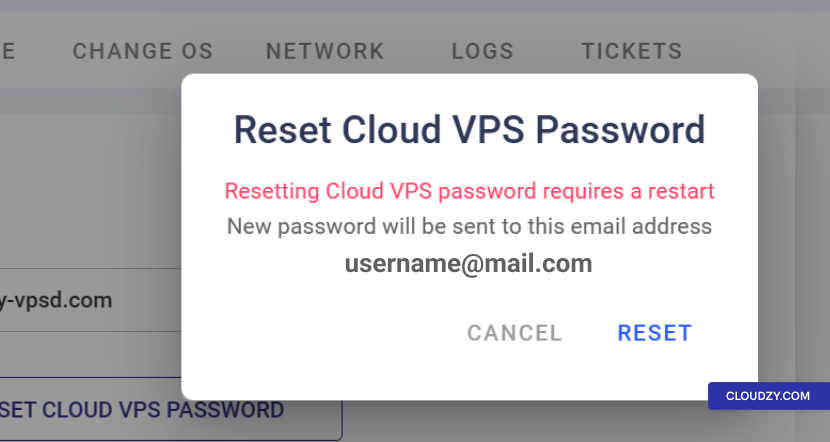
- Password Reset: Within the Cloudzy Panel, navigate
to the Access tab and click RESET CLOUD VPS
PASSWORD to generate a new password.
-
SSH Key Verification: In the SSH
Keys section of the panel, make sure that you enter your public
SSH key correctly. The path to the authorized_keys file
on your server, which should contain your public key, is typically
~/.ssh/authorized_keys. -
Permissions Check: On the server, confirm the
permissions of your ~/.ssh directory and the
authorized_keys file with chmod 700
~/.ssh and chmod 600
~/.ssh/authorized_keys.
Adjusting SSH
Configurations
For configuration adjustments:
-
Review and edit the SSH server configuration file located at
/etc/ssh/sshd_config on the server. Verify directives
like PermitRootLogin yes and
PasswordAuthentication yes to make sure they match your
requirements. -
Restart the SSH service to apply changes with sudo
systemctl restart sshd.
Checking DNS
Configurations
Troubles with DNS configurations can lead to SSH connectivity
problems. Here’s how to verify DNS settings on both the client and
server sides:
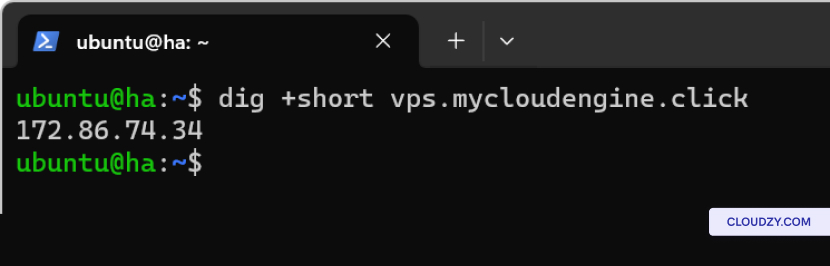
- On the Client Side (Linux): Use the dig command to
query the DNS records:
dig +short yourdomain.comThis should return the IP address of your server. If it doesn’t,
there’s likely an issue with the DNS resolution on your client
machine.
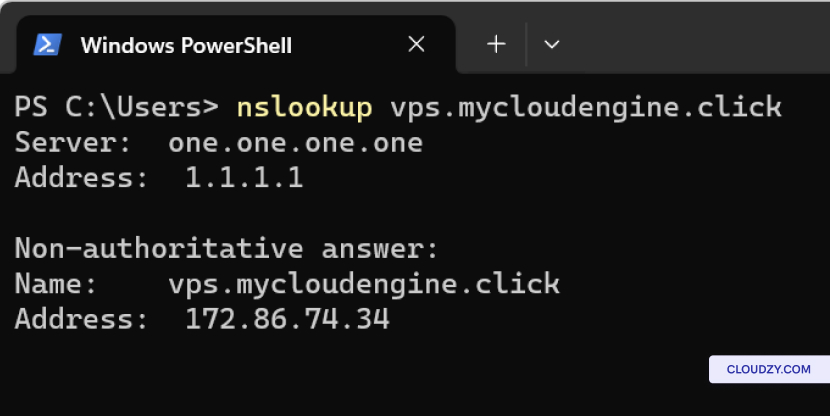
On the Client Side (Windows): Use
nslookup in the Command Prompt:
nslookup yourdomain.comSimilar to dig, this should return your server’s IP
address if DNS is resolving properly.
- On the Server Side: Check the DNS resolver
configuration file, typically /etc/resolv.conf, to make
sure that it points to the correct DNS server. It should have entries
similar to the following:
nameserver 8.8.8.8
nameserver 8.8.4.4These are Google’s public DNS servers and can be replaced with those
provided by your hosting service or ISP.
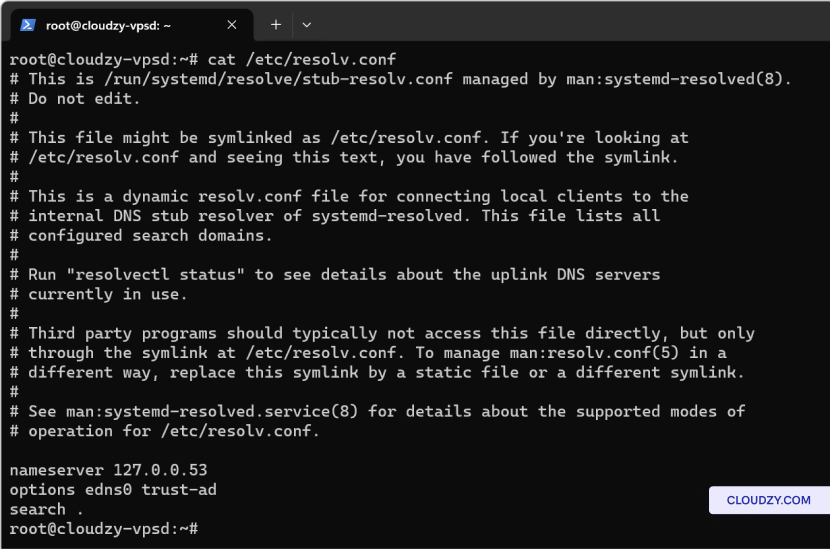
- Testing DNS Resolution on the Server: Use the
dig or nslookup command directly on
the server to ensure it can resolve domain names to IP addresses. If it
can’t resolve external domain names, this could indicate a problem with
the DNS service or network configuration on the server itself.
Monitoring Resources
with htop
Install htop for real-time monitoring:
-
Ubuntu: sudo apt-get install htop
-
CentOS: sudo yum install htop
Use htop to observe CPU, memory usage, and manage
processes directly within the interface.
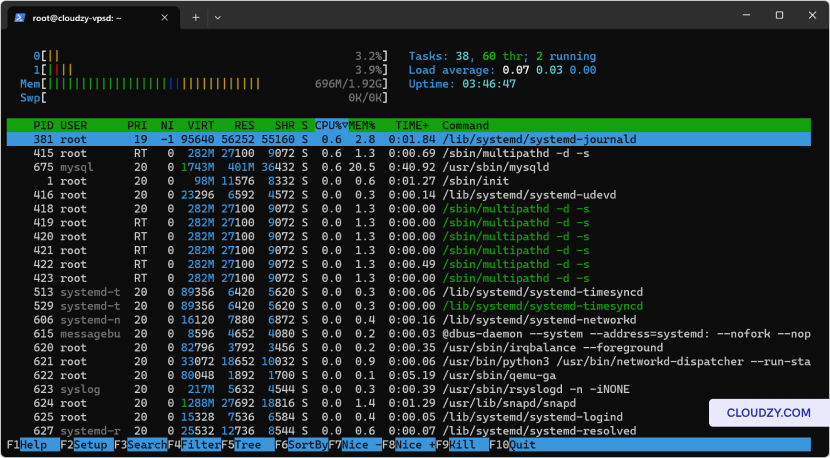
Maintaining Server
Health
Keep the server updated to prevent security vulnerabilities and
performance issues:
-
Ubuntu: Execute sudo apt update && sudo apt
upgrade to update all packages. -
CentOS: Run sudo yum update to refresh the
system.
To effectively resolve SSH connectivity issues, methodically check
and correct DNS settings, authenticate credentials, adjust firewall
rules, and review SSH configurations. Regularly updating systems and
monitoring resources are essential practices for maintaining a stable
and secure server environment. By adhering to these steps, you can have
reliable SSH access to your VPS, minimizing downtime and enhancing
security. If you need any more information or further assistance, feel
free to contact our support team by submitting a
ticket.