The SSH shell environment acts as the interface between users and the
remote server and enables command execution and system management over a
secure channel. Unfortunately, many users face various challenges within
this environment. These challenges include misconfigured shell settings,
such as an incorrect default shell or profile scripts and environment
variables that don’t behave as expected. Terminal emulation issues and
file permission errors can make the user experience even more
complicated. Addressing these issues is essential for efficient remote
server management and maintaining the integrity of SSH sessions.
Prerequisites
-
Basic understanding of the SSH protocol and its
operation. -
Access to the remote server with the necessary privileges to
modify shell settings. -
Knowledge of editing text files in a command-line environment
using editors like vi, nano, or
emacs. -
Access to a local terminal, an SSH client like PuTTY (for Windows
users), or the default terminal (for Unix/Linux/macOS users).
Common SSH Shell
Environment Issues
Incorrect Shell
Settings:
When a user logs into a remote server via SSH, the server invokes the
user’s default shell specified in /etc/passwd. Issues
may arise if this shell is set incorrectly or if the shell’s
configuration files (like .bashrc for Bash or
.zshrc for Zsh) contain errors. These files control the
shell’s behavior and environment settings; errors here can cause alias
malfunctions, incorrect path settings, or even prevent the shell from
starting.
Environment Variable
Problems:
Environment variables like PATH,
HOME, and EDITOR dictate the user’s
operating context and preferences. Misconfiguration can lead to commands
not being found, incorrect file editing, or scripts failing to run. Such
problems often originate from mistakes within the shell’s profile
scripts (/etc/profile or
~/.bash_profile).
Terminal Emulation
Errors:
SSH clients emulate a terminal to interact with the remote shell,
translating user inputs into commands and displaying output. If the
emulation settings and the server’s expectations (like using wrong
character encoding or incorrect terminal types) don’t match, users
experience garbled text, unresponsive sessions, or keybindings that
don’t function well.
File Permission
Issues:
The Unix file permission system controls access to files and
directories. If permissions are too restrictive, users may be unable to
execute scripts or access configuration files. On the other hand,
permissions that are too lax can pose security risks. Common permission
issues include .ssh/authorized_keys not being readable,
which can lead to public key authentication failure or crucial
executables lacking execute permissions.
Understanding these issues is the first step to troubleshooting SSH
shell environment challenges. Each component within the SSH environment
plays a crucial role, and misconfigurations can lead to significant
productivity loss or security breaches.
Diagnosing Shell
Environment Issues
Identifying
Configuration Errors:
Errors in shell configuration files can be tricky to spot. Check the
.bashrc, .profile, or equivalent
configuration files for syntax errors or incorrect settings. Look out
for missing punctuation, such as semicolons or quotes.
Checking Environment
Variables:
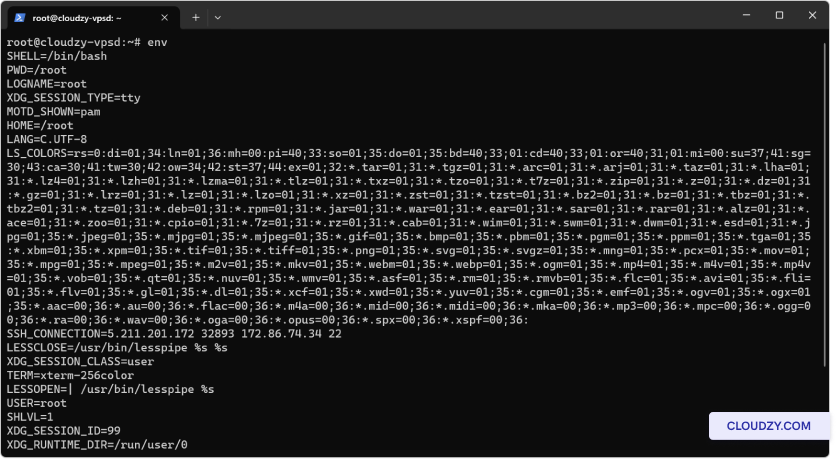
Use env, set, or echo
$VARIABLE_NAME to list and review environment variables. Make
sure that paths and settings are correct. For instance, the
PATH variable should include directories where commonly
used programs are stored, like /usr/bin/.
Testing Terminal
Settings:
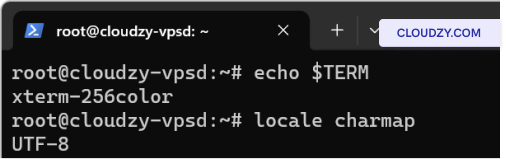
Verify that the terminal emulator is configured to match the server’s
settings. This includes checking the value of TERM, the
character encoding, and ensuring that locale settings (like LANG and
LC_*) are consistent across your local environment and the server.
Reviewing Server
Logs:
Server logs can provide valuable insights into SSH issues. The SSH
daemon log, typically located at /var/log/auth.log or
/var/log/secure, can include error messages related to
failed login attempts or configuration problems.
Diagnosing these elements can pinpoint the root causes of issues in
the SSH shell environment. Once identified, you can apply targeted fixes
to restore functionality.
Troubleshooting
and Solutions for SSH Shell Environment
Correcting Shell
Configuration:
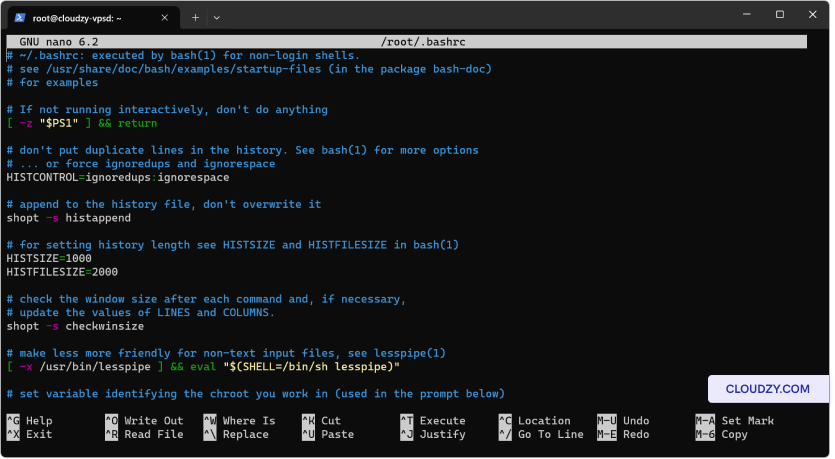
Check for syntax errors or misplaced commands in the shell
configuration files. To edit the .bashrc file, use
nano ~/.bashrc or vi ~/.bashrc. Look
for unclosed quotes, missing semicolons, or incorrect path statements.
For changes to take effect without logging out, type source
~/.bashrc.
Setting Environment
Variables:
Misconfigured or absent environment variables can be set correctly in
the .bashrc or .bash_profile files.
For example, to set the EDITOR variable to use nano,
add export EDITOR=nano to your
.bashrc. Then, apply the changes with source
~/.bashrc.
Adjusting
Terminal Emulation Settings:
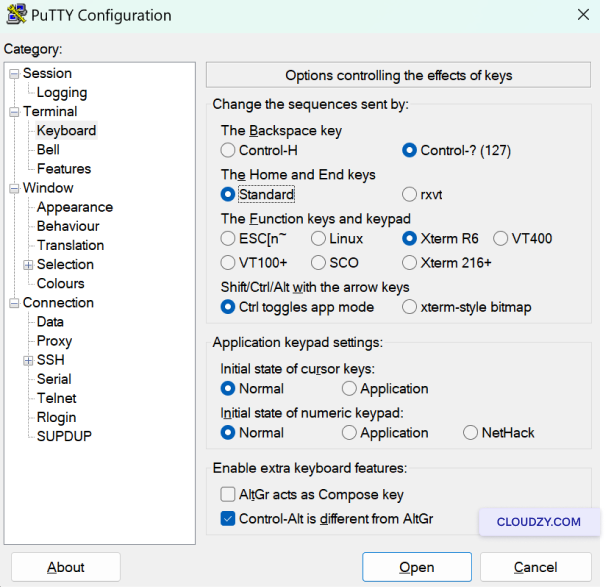
In your SSH client, check the terminal emulation settings. If you’re
using PuTTY, go to Terminal ->
Keyboard and ensure The Function keys and
keypad is set to Xterm R6. This will ensure
that your key presses are interpreted correctly by the server.
Fixing File
Permissions:
Correct file permissions are critical, especially for the
.ssh directory and its contents. To set the correct
permissions for the authorized_keys file, use:
chmod 700 ~/.ssh
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keysThese commands restrict read, write, and execute permissions
appropriately.
Reviewing Server Logs
for Errors:
SSH-related errors are typically logged in
/var/log/auth.log or /var/log/secure.
Use grep sshd /var/log/auth.log to filter SSH-related
messages. This can reveal issues with authentication, possible security
breaches, or other errors.
By applying these troubleshooting steps, you can resolve common SSH
shell environment issues and ensure a secure and efficient connection to
your server. If you need any more information or further assistance,
feel free to contact our support team by submitting a
ticket.