Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) serves as a critical tool for remote
administration, allowing users to control systems from afar. However,
its widespread use has made it a prime target for brute force attacks.
These attacks exploit weak passwords, attempting to gain unauthorized
access to systems. With the rise of remote work, securing RDP has never
been more crucial.
Comprehensive
Guide to Enhancing RDP Security
By adhering to the recommendations outlined below, you will bolster
the defenses of your remote desktop environment against unauthorized
access and cyber threats.
Renaming
the Administrator Account and Securing User Access
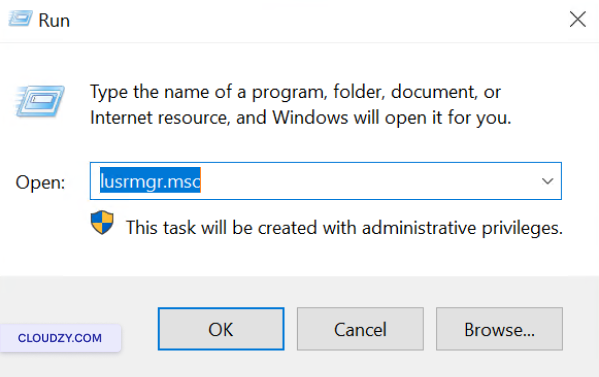
Press Windows key + R, type
lusrmgr.msc, and press Enter to open
the Local Users and Groups Manager.
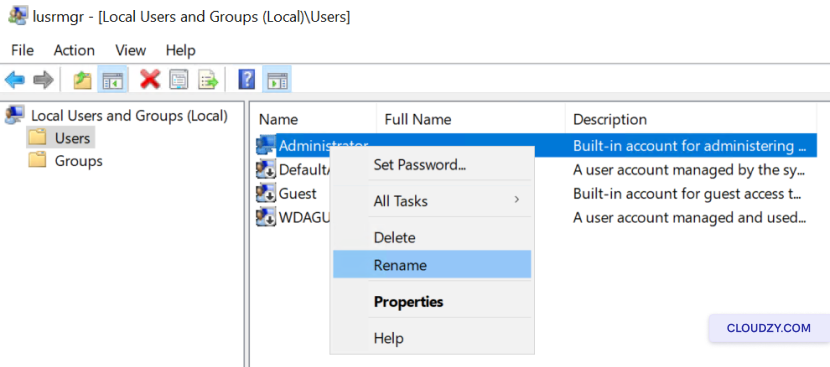
To rename the Administrator account:
- In the middle pane, right-click on the
Administrator account and select
Rename.
- Enter the new name for the administrator account and press
Enter.
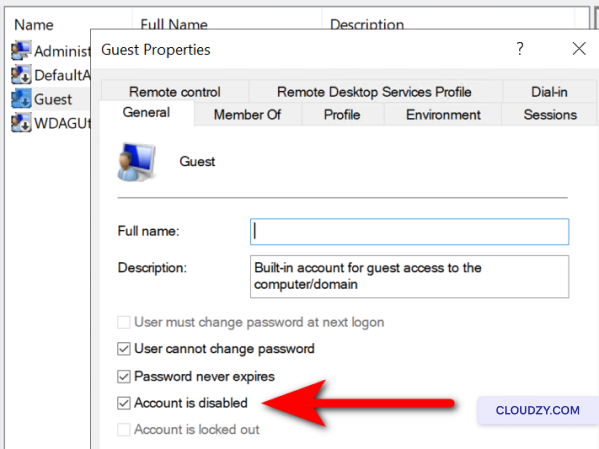
To disable the Guest account:
-
Find and double-click on the Guest account.
-
Tick the Account is disabled checkbox and click
on OK.
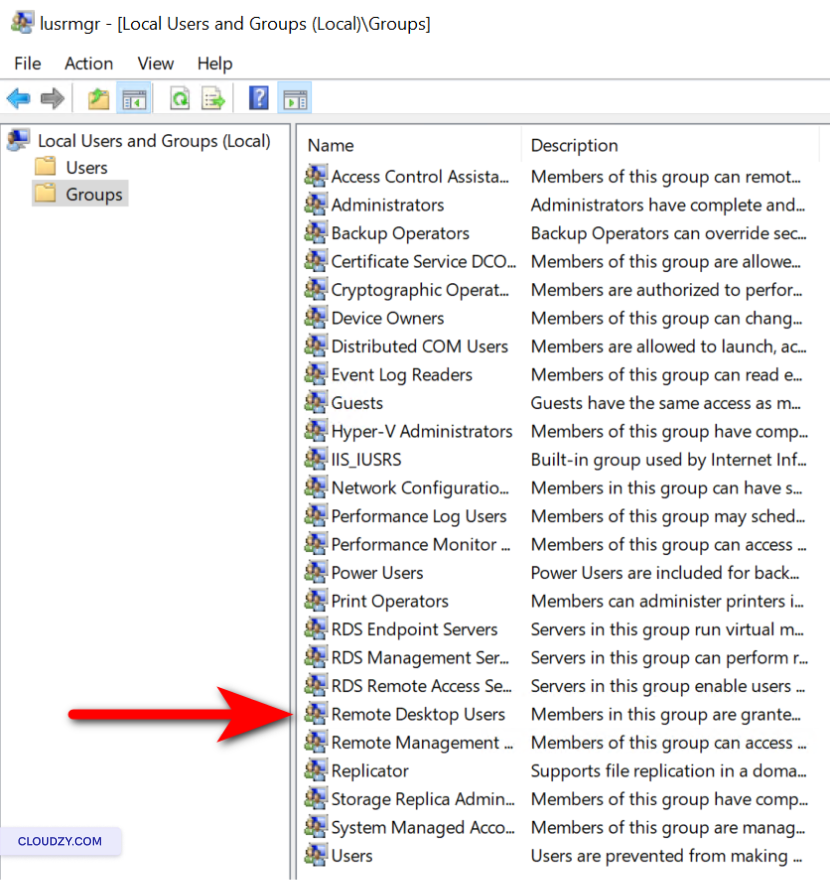
To regularly check RDP access permissions:
-
Click on Groups in the left pane.
-
Double-click on the Remote Desktop Users
group. -
Review the list for authorized users. To remove a user, select
them and click Remove. To add a user, click
Add and enter the necessary details. -
Click Apply and then OK to
confirm any changes.
Implementing a
Strong Password Policy
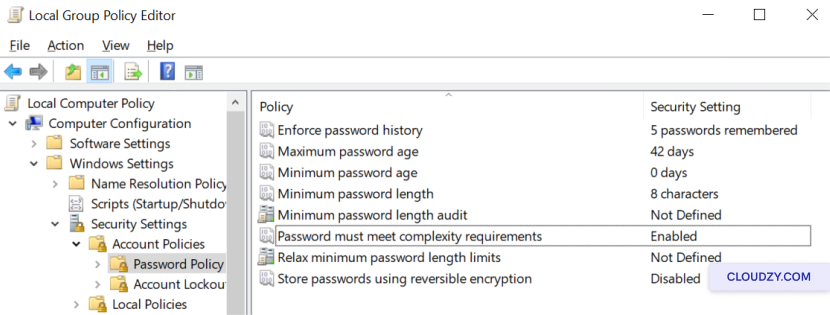
-
Open the Group Policy Editor by pressing Windows key +
R, typing gpedit.msc into the Run
dialog. -
Navigate to Computer Configuration > Windows Settings >
Security Settings > Account Policies > Password Policy. -
Define the minimum password length and complexity requirements to
enhance security. -
Enforce password history to discourage the reuse of recent
passwords.
Limiting
RDP Access via Firewall Configuration
-
Open Windows Firewall with Advanced Security by
typing wf.msc in the Run dialog (Windows key +
R). -
Click on Inbound Rules in the left
pane. -
Locate the rules for Remote Desktop – User Mode
(TCP-In) and Remote Desktop – User Mode
(UDP-In). -
Right-click each rule and select
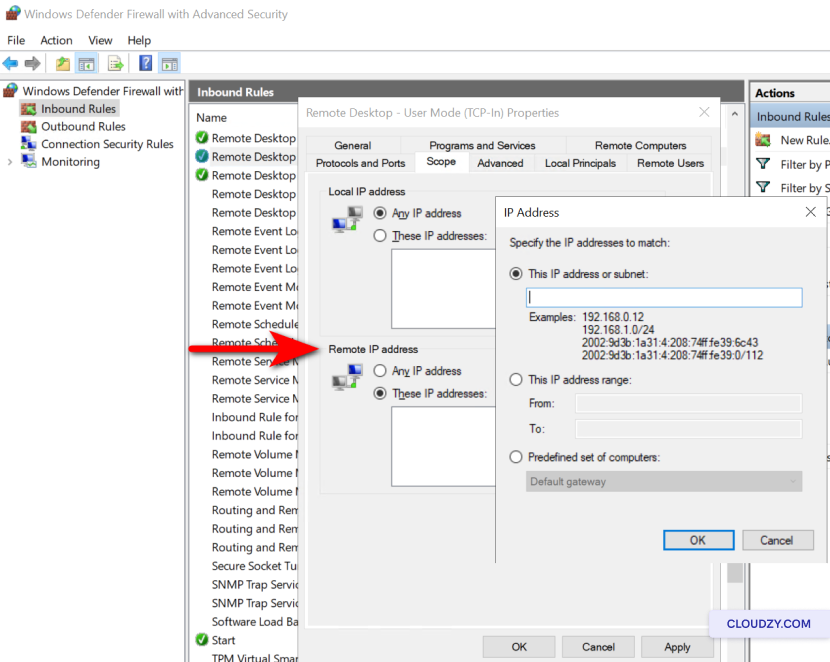
Properties. -
Under the Scope tab, click on These IP
addresses in the Remote IP address
section. -
Click Add and specify the IP addresses that are
permitted to establish RDP connections. -
Confirm the changes by clicking OK and ensure
the rules are enabled.
Setting Up
Multi-Factor Authentication
-
Choose an MFA solution compatible with your RDP setup (e.g., Duo Security, Microsoft
Entra). -
Follow the specific MFA provider’s installation and configuration
guide to integrate it with your RDP environment. -
Enroll users and set up secondary authentication methods like
mobile apps or hardware tokens.
Enabling Network
Level Authentication
- Right-click on This PC and select
Properties.
-
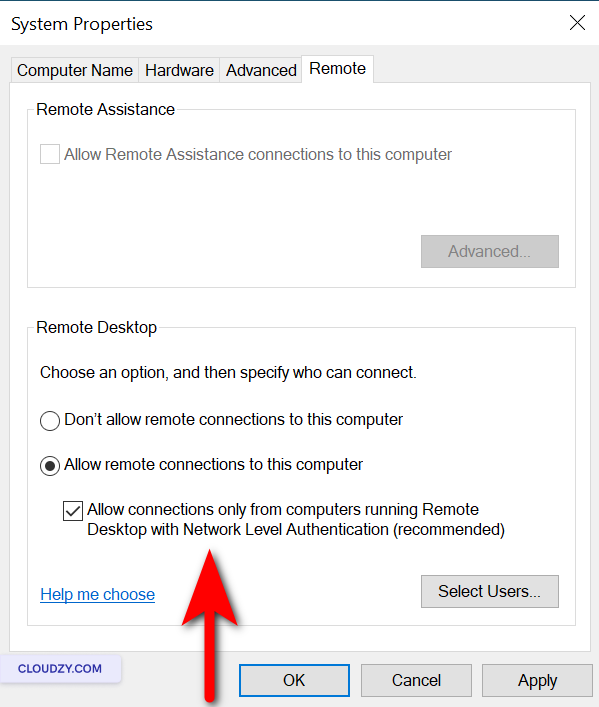
Click on Remote settings.
-
Under Remote Desktop, ensure Allow
connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network
Level Authentication is selected.
Changing the Default RDP
Port
-
Press Windows key + R to open the Run
dialog. -
Type regedit and press Enter to
open the Registry Editor. -
Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINEServer-Tcp.
-
Find the PortNumber subkey, double-click it,
select Decimal, and enter a new port number.
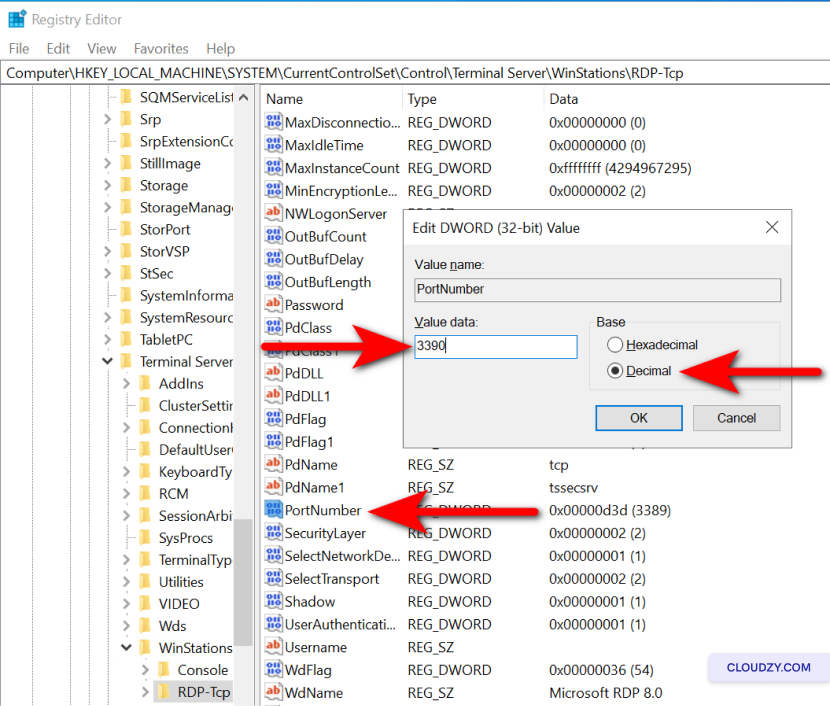
- Click on OK, close the Registry Editor, and update
your firewall rules accordingly.
Now, to allow the new port through the Windows
Firewall:
-
Open the Windows Firewall by pressing Windows key +
R, typing wf.msc. -
In the left pane, click on Inbound
Rules. -
Click on New Rule on the right pane.
-
Select Port and click on
Next. -
Choose TCP and specify the new port number you
set in the Registry Editor, then click Next.
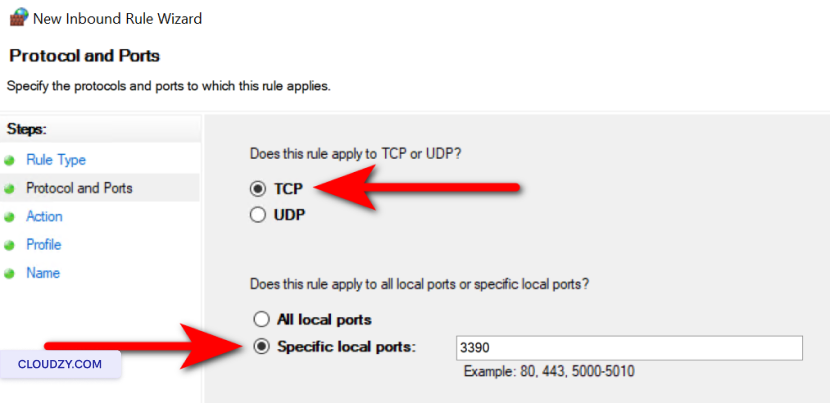
-
Select Allow the connection and click on
Next. -
Ensure Domain, Private, and
Public are checked to define the rule’s scope as
needed, then click Next. -
Give the rule a name, such as Custom RDP Port,
and click on Finish. -
Restart the system and then make sure to connect via the new
port.
Configuring
Account Lockout Policies
-
Access the Group Policy Editor by pressing Windows key +
R and typing gpedit.msc. -
Navigate to Computer Configuration > Windows Settings >
Security Settings > Account Policies > Account Lockout
Policy. -
Set the Account lockout threshold, Account lockout
duration, and Reset account lockout counter
after,to appropriate values.
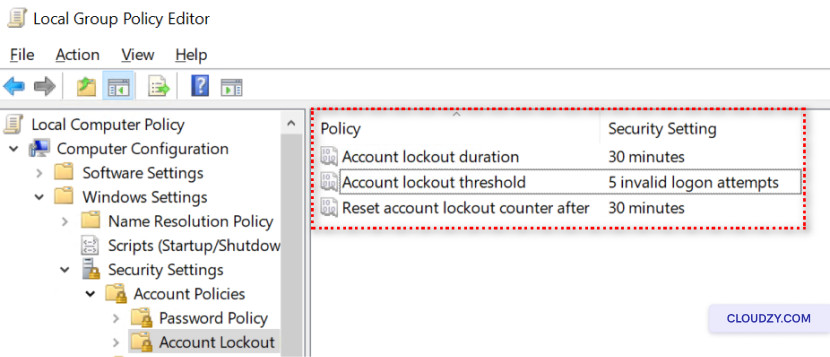
Updating Systems and
Software
-
Enable automatic updates in Windows Update settings.
-
Regularly check for updates on all software used in conjunction
with RDP. -
Apply updates during scheduled maintenance windows to minimize
disruption.
Deploying
Antivirus and Anti-Malware Solutions
-
Select a reputable antivirus and anti-malware software.
-
Install the software following the manufacturer’s
instructions. -
Set the software to update automatically and perform regular
scans.
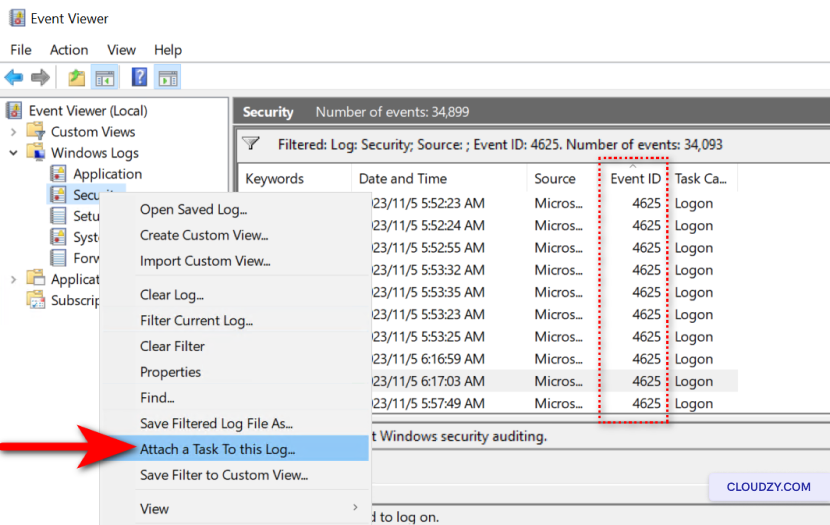
Conducting
Regular Security Audits and Setting Up Alerts
-
Open the Event Viewer by typing eventvwr.msc in
the Run dialog (Windows key + R). -
Navigate to Windows Logs > Security and look for event ID
4625. -
To set up alerts, right-click on Security and
select Attach Task To This Log…. -
Follow the wizard to create a task triggered by multiple
instances of event ID 4625.
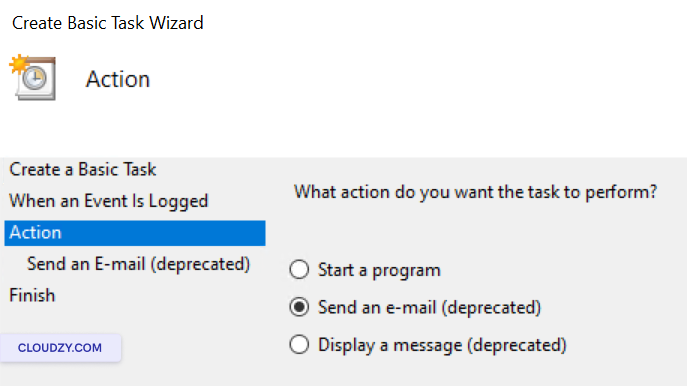
- Choose an action like sending an email or displaying a message when
the task is triggered.
- Complete the wizard and name the task for easy identification.
Using VPNs for
Additional Security
-
Determine the need for a VPN based on your security requirements
and the sensitivity of the data being accessed via RDP. -
Select a reputable VPN service provider or set up your own VPN if
you have the capability. -
Install and configure VPN client software on all devices that
will use RDP. -
Train users to connect to the VPN before initiating an RDP
session to ensure that the remote desktop traffic is encrypted and
secure. -
Regularly update and maintain the VPN infrastructure to address
any security vulnerabilities and ensure that it remains robust against
threats.
Fortify your RDP like a digital fortress. Regular updates and best
practices are your vigilant sentinels, ensuring your network’s defenses
remain impenetrable. Stay alert and proactive—your cybersecurity depends
on it. If you have any questions, don’t hesitate to contact our support
team by submitting a
ticket.